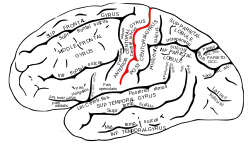
Central sulcus Definition
It is a furrow or deep groove in the brain. It is said to have a ‘map’ of the body on each side that matches the other side.
It is also known as “Fissure of Rolando” or “Rolandic Fissure,” after the noted Italian anatomist Luigi Rolando.
Central sulcus Location
It is located at a medial position of the lateral surface of the cerebral hemisphere. It is just anterior to the ascending cingulate.
Central Sulcus – Development in Brain
As soon as a fetus turns 5 to 6-month old, the central sulcus starts to develop. It means that the embryo marks the origin of its development in the brain. It grows towards the superior margin that is present in the cerebral hemisphere. The growth reaches a definite stage when the fetus grows almost 8-month old.
Parts of Central Sulcus
Fissures & Sulcus
There are multiple convoluted medial and lateral and surfaces that comprise the cerebral cortex of the brain. These build up the surface area of the brain, thereby increasing the number of neurons over there. The neurons give rise to deep and shallow furrows in the region. The deep furrows are referred to as fissures while the shallow furrows are called sulci or sulcus.
Gyrus
Also known as Gyri, these are the ridges that are found between the brain’s sulcus.
Lobes
The gyri and vital fissures of the brain are divided into four distinct parts, which are known as lobes. When it comes to elaborating the central sulcus well, studying the four lobes that constitute the human nervous system is important. The four lobes include the frontal lobe, parietal lobe, temporal lobe, and occipital lobe.
Frontal Lobe
The frontal lobe is found in the front side of the central sulcus. The precentral gyrus is present right in front of it (central sulcus). This gyri acts as central cortex’s primary motor region. The rest of this lobe is further divided into superior frontal gyri, middle frontal gyri, and inferior frontal gyri.
Parietal Lobe
Parietal lobe is found in the posterior part of the central sulcus. It is considered as the main site where the primary somatosensory cortex lies. The postcentral gyrus is found in the most interior part of the lobe. Furthermore, the intraparietal sulcus divides the lobe into superior parietal lobules and inferior parietal lobules. The divisions are found behind the postcentral gyrus.
Temporal Lobe
It is present beneath the lateral fissures, which run parallel to them. The temporal lobe gets divided into three principle gyri on the lateral side – superior temporal gyri, middle temporal gyri and inferior temporal gyri.
Occipital Lobe
The boundary dividing the occipital lobe and the parietal lobe is finely marked on the medial surface by the deep parieto occipital sulcus. The presence of this lobe in the medial surface is the only landmark it has. There is no identifiable mark that can distinguish this lobe.
Limbic Lobe
Besides the above four lobes, there’s a fifth one that consists of portions of all the four lobes in and around the central sulcus. Some portions of the frontal, parietal, and temporal lobes form the limbic lobe. The system connecting the cingulated gyrus, parahippocampal gyrus, and hippocampus gyrus is referred to as the limbic lobe.
Central sulcus Function
Its primary function is to separate the parietal lobe of the cerebral cortex from the frontal lobe. The parietal lobe also referred to as the Parietal cortex, is the section of the cerebral cortex in either brain hemisphere that is situated under the crown of the head. The frontal lobe, on the other hand, is positioned exactly behind the forehead.
It also separates the primary somatosensory cortex from the primary motor cortex.
- Central sulcus enables to identify the different crucial parts surrounding the brain.
- It separates the sensory areas from the motor regions of the brain
- The central sulcus plays an important role in neurosurgery as it serves to be a guide in identifying the brain’s cortical areas.
- If neurosurgeons are unable to identify the central sulcus at the time of epilepsy surgery, the patient might suffer from memory loss, motor, intellectual, and personality disorders
Central Sulcus – Medical Examination
To examine the central sulcus, Magnetic Resonance Imaging scanning can be done. Though there is no fluid or tissue present inside the region, MRI scan can still be helpful. The type of cerebrospinal fluid in the region will determine the colour of the central sulcus, which may range from dark to bright. The scanning will help identify if there’s an issue with the functioning of the brain or structure.
The signs that will help you identify central sulcus in an MRI scan include:
- Midline Sulcus sign: This appears as the longest running horizontal elemental, entering the interhemispheric fissure. This is the central sulcus.
- Inverted omega sign: It helps you identify where the central sulcus is.
M sign: The “M” pattern that is seen in the scan results is the central sulcus
Central sulcus plays a very important role whether it is about identifying different brain parts or its part in neurosurgery. Hence, knowing about it in details is mandatory.
Central sulcus Pictures
Here are some useful pictures of Central sulcus that you may find assistive for reference.
Picture 1 – Central sulcus
Picture 2 – Central sulcus Image
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Central_sulcus
http://www.merriam-webster.com/medical/central%20sulcus
http://culhamlab.ssc.uwo.ca/fmri4newbies/PrimeronCorticalSulci.html#Central%20sulcus
http://serendip.brynmawr.edu/bb/kinser/definitions/def-csulcus.html

No comments yet.