Papillary muscle Definition
It refers to a tiny muscle inside the heart that serves as an anchor for the cardiac valves. There are two muscles of this type, which are named according to their position in the heart –
- Anterior Papillary muscle
- Posterior Papillary muscle
Papillary muscle Location
As aforesaid, these muscles can be found in the heart. The muscles of the right ventricles, three in number, arise in the ventricular wall. The muscles anchor themselves to the cusps or flaps of the atrioventricular valves, such as the tricuspid and mitral valve through the chordae tendineae.
Papillary muscle Function
The muscle contracts to avert prolapse or inversion of the atrioventricular valves. The Papillary muscles located in the left and right ventricles start contracting shortly prior to the ventricular systole. The contraction is maintained all through, which prevents backflow (regurgitation) of the blood of the ventricles into the atrial cavities.
In the absence of these muscles, tricuspid regurgitation can occur.
Papillary muscle Disorders
A rupture or dysfunction of these muscles, as can be caused by a heart infarct and Ischemia (respectively), can give rise to a complicated condition known as Mitral Valve Prolapse.
Papillary Muscle Rupture
This is the condition that arises when the muscle tears or is found in any chordate tendineae. It is tendon-like “strings of heart” that established a connection between the papillary muscles and atrioventricular valves. In this condition, the flow of the blood is regurgitated back and forth to the atrium via the valves. This reiteration causes serious complications due to the lack of blood flow into the ventricles.
Papillary Muscle Symptoms
- High blood pressure
- Increased heart rate
- Shortness of breath
- Insufficient blood flow
- Pulmonary edema, which refers to the buildup of fluids in the lungs
Papillary Muscle Causes
- It normally occurs after a heart attack. The condition is often overlooked after the attack but it can be life-threatening.
- Insufficient oxygen and blood flow to the cardiac muscles
- Inadequate blood flow
- Ischemia, a condition in which the blood flow to the tissue is insufficient in the body
Papillary Muscle Diagnosis
As already stated, the rupture is generally diagnosed post-myocardial infarction. Hence, the pulmonary examination is the first thing conducted to identify the condition. Besides it, the physician may suggest chest X-rays, electrocardiograms or ECG. Through the ECG, the atrial enlargement can be detected, which indicates the valve regurgitation.
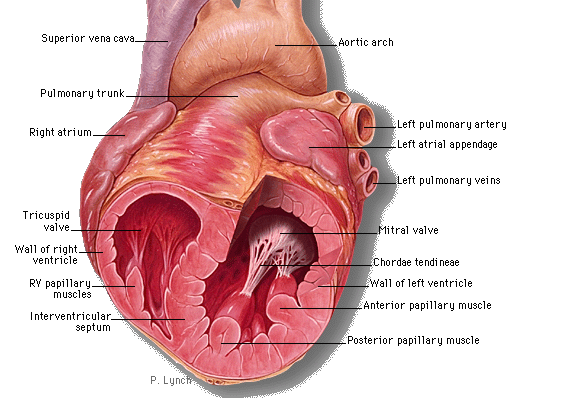
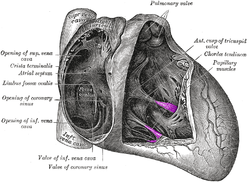
Papillary muscle Pictures
Take a peek at these assistive images to know about the physical appearance of this cardiac muscle.
Picture 1 – Papillary muscle
Picture 2 – Papillary muscle Image
References:
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Papillary_muscle
http://www.medterms.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=4755
http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/papillary+muscle
http://www.vhlab.umn.edu/atlas/rv/papillary/index.shtml

No comments yet.