Our brain is the most complicatedly structured part of the body. The right and the left hemispheres of the brain perform definite functions and maintain sync between different body parts, thereby producing different sensations in the body.
While the left brain takes care of the right side of the human body, the right hemisphere of the brain controls the left side of the body. With the left brain, you become more verbal, analytical and logical whereas the right brain makes you more intuitive, imaginative, rhythmic, and a person with a holistic thought-process.
Corpus Callosum Definition
The right hemisphere and the left hemisphere both serve the human body by making them work in a proper sync while having different perceptions towards the same thing. Corpus Callosum bridges this gap between the two hemispheres of the brain.
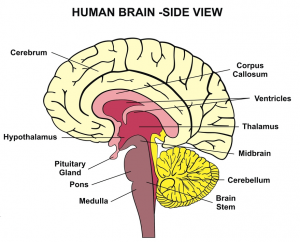
Corpus Callosum is the part of the brain that connects the right and left hemispheres of the brain. It enables proper communication between the two hemispheres of the brain. It is a large, C-shaped bundle of nerve fibers, which stretches across the midline of our brain. It develops the largest collection of white matter tissue that is commonly found in the brain.
Corpus Callosum Location
It is located above the Thalamus and below the cortex.
Corpus Callosum Divisions
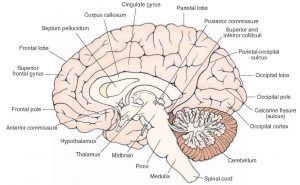
The corpus callosum moves from the anterior i.e. the front part to the posterior i.e. the back part of the brain. It can be divided depending on the regions it needs to functions. These regions include rostrum, genu, body, and splenium.
While the rostrum and genu connect the frontal lobes of the left and the right brain, the body and the splenium connect the temporal lobes of the hemispheres as well as the occipital lobes.
Function of Corpus Callosum
The functions of the corpus callosum are:
- It sends neural messages between the right and left hemispheres
- It creates a useful view of the world
- It transfers motor, sensory, and cognitive information between the two hemispheres
- It helps in the eye movement and vision
- It maintains the balance of arousal and attention
- It localizes the tactile information between the two hemispheres, thereby helping to locate touch sensation
- It enables individuals to identify an object by connecting the visual cortex with the brain’s language centers
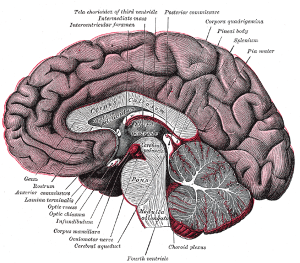
Corpus Callosum Pictures
Agenesis of the Corpus Callosum
Agenesis of the corpus callosum or AgCC is a condition in which a person is either born with a partial corpus callosum or no corpus callosum at all. The structure develops in an individual between 12 to 20 weeks and undergoes structural changes until a person attains adulthood.
Known Causes
- Chromosome mutations
- Prenatal infections
- Genetic inheritance
Abnormal Effects on Brain
- Hydrocephalus, or fluid in the skull
- Deep clefts in brain tissue
- Neural migration disorders
- Arnold-Chiari malformation
- Failure of the forebrain to divide into lobes
Syndromes
- Menkes
- Andermann
- Shapiro
- Aicardi
- Crocallosal
- Mowat-Wilson
- FG
Diagnosis
AgCC can be diagnosed usually within the first two years of a person’s life. The first sign of a brain dysfunction is an epileptic seizure while the disorder may remain undetected for a couple of years in some cases. The tests that can be conducted to identify the disorder are listed as follows:
- Prenatal ultrasound
- CT scan
- MRI scan
Symptoms
The signs and indications of the Agenesis of the corpus callosum can be divided into four categories – Physical, Mental, Developmental, and Social and Behavioral.
Physical Signs
- Vision issues
- Feeding difficulty
- High tolerance for pain
- Sleeping disorders
- Low muscle tone
- Abnormal head and facial features
- Seizures
- Hearing issues
- Chronic constipation
Mental Signs
- Problem-solving difficulty
- Difficulty in understanding emotions
- Problems in reading facial expressions or voice tones
- Lack of risk-assessing ability
- Issues in understanding abstract concepts
- Problems in understanding slang or sarcasm
- Untrue information delivery and believing it’s true
Developmental Issues
- Delay in speech and language acquisition
- Delay in sitting, walking, riding vehicle, etc.
- Delayed toilet training
- Clumsiness and poor coordination
Social and behavioral
- Lack of self-awareness
- Social immaturity
- Hyperactivity
- Lack of fear
- Difficulty in understanding social cues
- Finding it hard to maintaining attention
- Problems understanding others’ perspectives
- Hard to maintain attention
- Obsessive or compulsive behavior
Another condition that arises because of the corpus callosum is Spina Bifida. This condition is reported when the spine does not fuse properly, thereby leaving a defect in the spinal canal.
FAQs
What is a callosal disorder?
This is the condition in which the corpus callosum does not develop in a typical manner. It can only be diagnosed by brain scan.
What is Dysgenesis of the Corpus Callosum?
This is the condition that means that the corpus callosum developed but in some incomplete way. Thus, partial Agenesis of Corpus Callosum and Hypoplasia of the Corpus Callosum can be considered as forms of dysgenesis, which identifies the inadequate development of the callosal.
What are the effects of severing the corpus callosum?
It enables the sharing of the information via the brain hemispheres. However, the same contributes to the spread of the seizure impulses from one side of the brain to another. The process of corpus callosotomy is about making the cuts (severs) to the corpus callosum that interrupts the spread of the seizures.
What is a split-brain syndrome?
It is the condition identified by a cluster of neurological abnormalities that arise from the partial or total severing or lesioning of the corpus callosum. It is also referred to as callosal disconnection syndrome.

No comments yet.