What is the Cribriform Plate?
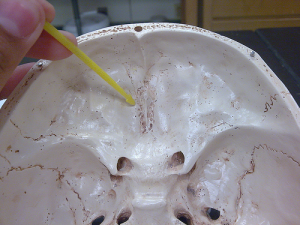
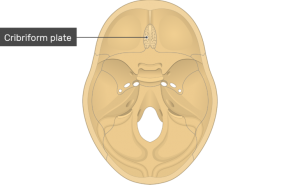
In the human skull, Cribriform Plate is a significant part that separates the brain from the nasal cavity. It is like a honeycomb or sieve-like structure that is thin and narrow and has tiny perforations. This plate which is situated between the anterior cranial fossa and the nasal cavity is a part of the ethmoid bone that supports the olfactory nerves. These nerves run through the tiny perforations situated in Cribriform Plate and provide with a sense of smell to humans. The Cribriform Plate forms the roof of the nasal cavity. The crown of the eye sockets is situated at the sides of this plate.
Cribriform Plate Structure
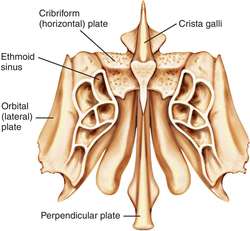
The structure of the Cribriform Plate is complex but not baffling one. The human skull comprises of the ethmoid bone which is a singular porous bone that forms the midfacial region of the skull. It adds to the molding of the nasal septum orbit and the nasal cavity. This bone comprises a perpendicular plate and two ethmoid labyrinths that are attached to the Cribriform Plate. This perpendicular plate runs horizontally from the Cribriform Plate and attaches itself to the septal cartilage of the nose.
Cribriform Plate Location
From the middle line of the Cribriform Plate runs a thick, smooth, triangular progression that projects upwards towards the human skull, this is called the crista galli.
The Cribriform Plate’s structure is narrow and deeply uneven and is located on either side of the crista galli. The plate provides support to the olfactory bulb which is perforated by foramina to serve as a passage to the olfactory nerves. The foramina are openings in the Cribriform Plate which create a passageway for the nerves that enables humans to smell and differentiate between odors. The foramina help in transmission of the olfactory nerves to the roof of the nasal cavity.
Function of Cribriform Plate
The plate provides support to the olfactory bulb which is perforated by foramina to serve as a passage to the olfactory nerves. The openings in the Cribriform Plate comprises of nerves that enable humans to smell and differentiate between odors.
Cribriform Plate Pictures
Cribriform Plate Injury
Cribriform Plate plays a crucial role in the human skull formation. Following are some interesting points on Cribriform Plate’s significance:
- In the case of a severe damage, such as a rupture or a fracture involving the Cribriform Plate, there can be problems like cerebrospinal fluid leakage. In such cases, instantaneous medical intervention is required. If treatment is delayed for a longer period of time then it could result in brain damage or even death. A fracture in the Cribriform Plate can even result in loss of smell.
- During any kind of damage or infections, the small opening of the plate that also transmits the olfactory nerve becomes directly accessible to pathogens which are called brain eating amoebas (Naegleria fowleri). The amoeba can then spread to the rest of the brain through the proliferation of trophozoites. To kill this pathogen, expert’s advice use of transcribrial route device that can destroy it at an area of maximum proliferation.
- During a head injury, there are fatal chances of damage to Cribriform Plate. Damages can even occur during surgical procedures in the areas surrounding the Cribriform Plate, mostly in surgical operations that involve treatment of sinuses.
Diagnosis
During damage to the Cribriform Plate and surrounding parts, the olfactory receptor cells become exposed to harmful viruses, bacteria, and dust particles which make the other body parts vulnerable to harmful substances present in the outer world. These substances can cause damage to:
1. Actual receptors
2. Nerve cells
3. Cells and tissues located in the head
Since olfactory nerve fibers pass through the Cribriform Plate, during a head injury, the force with which this injury comes can cause the fibers to crush and damage the cribriform plat as well. This can result in a potential effect on the sense of smell, this symptom of losing out on the sense of smell results in anosmia. Below is the list of the most common causes of anosmia that can damage the olfactory system that is supported by Cribriform Plate:
1. Nasal-Sinus Disease
2. Chronic sinus infections
3. Nasal polyps
4. Viral Upper Respiratory Infections
5. Head Trauma
6. Congenital anosmia
7. Some other causes include age-related diseases such as Parkinson’s Alzheimer’s disease
Due to the vulnerable position of olfactory receptor neurons, they are at risk of damage from pollutants and chemicals in the air. These can damage the olfactory receptor cells and surrounding parts. Exposure to a short and long term of chemical agents has been associated with smell troubles, which can be either momentary or everlasting. Hence the role of Cribriform Plate is crucial as any kind of damage from the environment/accidents or other types of injuries can result in cumulative casualties.
Frequently Asked Questions
What causes damage to cribriform Plate?
The olfactory nerves get crushed with a major force during an injury and damage the cribriform plate as well. Chronic sinus infection, head trauma, Alzheimer’s’ disease, Parkinson’s, congenital anosmia and other age-related diseases may cause vital damage to the Cribriform Plates.
Where is Cribriform Plate located in the human body?
The Cribriform Plate of the ethmoid bone is located in the frontal bone and roofs in the nasal cavities. The ethmoid bone comprises a perpendicular plate and two ethmoid labyrinths that are attached to the Cribriform Plate. This perpendicular plate runs horizontally from the Cribriform Plate and attaches itself to the septal cartilage of the nose.

No comments yet.