What is Tibialis Posterior Muscle?
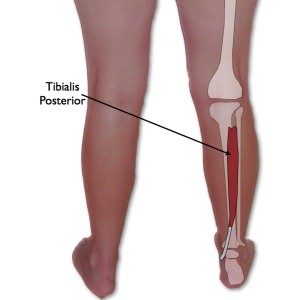
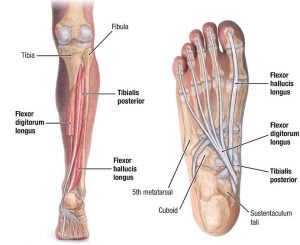
The tibialis posterior muscle is a relatively small, centrally located muscle present on the back side of the leg. This muscle is located between the two bones fibula and tibia in the lower leg and descends down to connect with the various other bones through the ankle. The tibialis posterior muscle originates from the proximal 2/3rd of the posterior side of the tibia and the fistula bone from the back side of the calf along with interosseous membrane.
The tendons of the tibialis posterior muscle descend towards the small protruding bone of the ankle (also known as medial malleolus) and finally ends by segregating into three different branches namely the main, plantar and recurrent respectively. The muscle is mostly involved in providing stability to the lower legs and helps in the foot movements as well as provides support to the medial arch of the foot. The blood supply to the tibial muscles is provided by the tibial artery and the tibial nerves innervate the muscles and help in proper functioning of the tibial posterior muscles.
Tibialis Posterior Location
The tibialis posterior muscle is located in the posterior region of the leg and is the most centrally placed leg muscle.
Tibialis Posterior Function
The tibialis posterior muscle plays a major role in supporting the medial arch of the foot, assisting in the plantar flexion of the ankle of the foot, contraction of the muscle to assist inversion in the foot as well as assisting in tendon stabilization.
Origin
The Tibialis posterior muscle originates from the posterior sides of the tibia and fibula.
Insertion
The tendon normally splits into two slips once it passes through the plantar calcaneonavicular ligament from the inferior side. The superior slip then further most of the time inserts into the navicular bone while other times it may often insert into the medial cuneiform.
The deeper slip further divides into two different slip that individually inserts into the metatarsals 2 and 4 through the plantar surface and the other one into the medial cuneiform.
Action
The Tibialis posterior muscle main action is the inversion of the foot, supination of the foot along with plantar flexes of the ankle, and adduction of the foot.
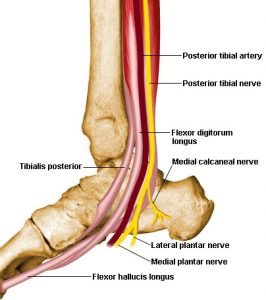
Innervation
The Tibial Posterior Nerve is innervated by L4 and L5 Tibial Nerve.
Blood Supply
The posterior tubular artery along with the muscular branches of the sural and peroneal provides the arterial or blood supply to the tibialis posterior muscle.
Tibialis Posterior Pictures
Tibialis Posterior Muscle Pain
The pain in the tibialis posterior muscle may initiate in the back of the lower leg, just above the heel or it may radiate further towards the heel and at the bottom of the foot. Some persons may experience the pain in the calf as well. This is because the muscle tendons attach to various bones present in the middle foot area while surrounding the inside of the heel.
The pain in the tibialis posterior muscles may be caused due to various activities like running or walking on the uneven surfaces, wearing improper footwear like worn shoes or sandals that pushes the foot inwards. The muscular pain is often experienced by athletes and sportspersons.
Tibialis Posterior dysfunction
Any kind of dysfunction caused to the tibialis posterior muscle may result in the deformity of the foot and leads to a muscular disorder known as “flat foot syndrome”. The tibialis posterior dysfunction is one of the most common disorders related to foot and ankle. However, many a time this dysfunction may be misdiagnosed as ankle or foot sprain, and by the time dysfunction of the muscle may be diagnosed by the foot specialist, the patient may be suffering from the disorder since many years. However, the patient may not require elaborate treatment procedures and most often the condition may be treated with simple exercises and use of few braces and orthotics.
Causes and Symptoms associated with the Tibialis posterior dysfunction
Any physical injury or damage caused due to the wear and tear of the tendon surrounding the ankle may cause the dysfunction of this muscle. Sometimes there may not be any specific cause for the wear and tear of the tendon. The dysfunction may be associated with the pain in the foot arch along with gradual flattening of the foot. The person may experience pain along with swelling in the foot. There may be visible deformity in the foot with the inward rolling of the foot. In extreme or severe cases, the person may also experience arthritis in the various joints of the foot.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosis of Tibialis Posterior dysfunction may be done by the physician by studying the symptoms along with the physical examination and if required X-ray and MRI scan of the area shall also be performed for proper examination.
The treatment procedures may involve non-operative treatment procedures, which may involve giving patient specially designed boots which immobilize the foot and ankle of the patient thus helping in providing rest to the damaged tendon. Later on, these special shoes may be replaced with specially designed insole for long-term use by the patient. In cases where the person may not be comfortable with the use of insole, they may use more sturdy and rigid custom designed shoes to help relieve the pain. In more serious conditions the doctor may suggest surgical procedures to repair the damaged tendon or to reconstruct the flat foot.
Tibialis Posterior FAQ’s
What is PTTD?
PTTD or Posterior tibial tendon dysfunction is also often referred with various other names like Tibialis Posterior Syndrome; Posterior tibial insufficiency; Adult acquired flatfoot; or Posterior tibial tendon syndrome. This is caused due to the damage of the muscle resulting in the deformity of the foot. This condition may also be sometimes confused with other dysfunction know as Tibialis posterior tendinopathy.
What is TPT and how it differs from PTTD?
The TPT (tibialis posterior tendinopathy) is a condition where degenerative or a painful injury may be caused by the tendon associated with tibialis posterior muscle. While in PTTD the damage is caused to the muscle itself.
What general treatments are suggested to relieve PTTD pain?
If the condition is not severe, certain simple exercises as suggested by the physician helps a lot in relieving the pain as well in improving the movement of the foot in case of tibialis posterior dysfunction.
What exercises shall be done to relieve PTTD pain?
The foot movements may be tried to be recreated with the help of an elastic band. The elastic rehab band may be looped around the midfoot and then tried to pull down on the sides. Further, the sole shall be moved inwards so that the foot comes in inversion position with the toes pointing downwards as in the plantarflexion position. The difficulty level may also be increased by increasing the strength of the elastic rehab band.

No comments yet.