Pharyngeal tonsil Definition
It refers to a lump of lymphoid tissue that comprises of cells involved in killing off pathogenic beings. They are part of the immune system along with tonsils. However, unlike tonsils, they are not directly visible by looking at the back region of the throat.
Pharyngeal tonsil Synonyms
It is also referred to as:
- The Third tonsil
- Adenoid
- Nasopharyngeal tonsil
In Latin, it is also known as Tonsila pharyngea.
Pharyngeal tonsil Location
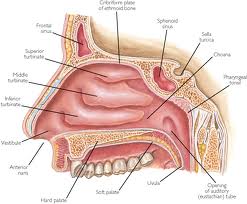
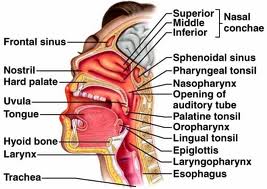
It can be found in the back end of the nasal cavity, in the roof of the nasopharynx. This is the region where the nose mingles with the throat. In children, it usually forms a soft lump in the posterior wall and the roof of the nasopharynx, in a position immediately above and behind the uvula.
Pharyngeal tonsil Development
Subepithelial infiltration of lymphocytes during and later than the 16th week of embryonic development forms pharyngeal tonsil and its enlargement starts and continues until 5 to 7 years of age.
Pharyngeal tonsil Functions
Much like other tonsils, the aim of Pharyngeal tonsils is to increase the capability of the lymphatic system against foreign organisms which enter the body through the nose and mouth and pass into the throat. In infants, inflammation of these tonsils acts as a natural defense against infections.
As children become older they develop other ways of combating infections. Pharyngeal tonsils start to shrink by 5 years of age and almost disappear by teenage.
Pharyngeal tonsil Disorders
Pharyngeal tonsils undergo temporary swelling when trying to combat infection by trapping the infectious agents. Swelling reduces over a period of time when infection subsides. However, sometimes it remains enlarged even after infection reduces and other times pharyngeal tonsils themselves get infected, a condition known as adenoiditis.
Adenoiditis can result from infections caused by a number of viruses like rhinovirus, and Epstein-Barr virus, and adenovirus. Bacterial strains like Streptococcus can also cause infection. Allergies also cause enlargement of adenoids.
An enlargement of these tonsils also called as adenoid hypertrophy, can significantly block the airways and give rise to various health issues, such as snoring and breathing through the mouth.
Enlargement of these tonsils may also lead to other problems like:
- Sinusitis- sinus cavities are hollow, air-filled regions in facial bones surrounding nose and eyes may fill up with fluid and become infected. Fluid can get accumulated in these cavities and cause infection.
- Chronic colds
- Nasal sound during talking appears as the person is talking with a pinched nose
- Bronchitis- if pharyngeal tonsils have severe viral or bacterial infection, then the infection can spread to other regions such as the lungs, bronchioles, and other respiratory organs.
- A sore throat or dry throat resulting from breathing through the mouth
- Difficulty in swallowing
- Sleep apnea
- Difficulty in sleeping
- Stuffy and blocked nose
Increase in tonsil size may block the Eustachian tubes or add more pressure on them. These tubes join the nasopharynx to the ears. An increase in pressure on these tubes, or their obstruction, may lead to the inflammation of the tympanic membrane of the ear. This can give rise to a painful ear condition known as Otitis media. If left without treatment, this disorder may lead to loss of hearing. Naturally, surgical procedures are recommended for curing this condition.
Adenoiditis Diagnosis
An otolaryngologist will usually begin the diagnosis by enquiring about the symptoms and then it followed by a physical examination. During the examination, family history is also taken into account to rule out hereditary. With help of a special mirror, the doctor will insert a small, flexible telescope, an endoscope, via the nose and view the adenoids.
Based on the examination, a blood test could be needed to assess the type of infection. Alternatively, throat tests using swabs can also be performed for obtaining and analyzing the bacterial or other organisms causing infection.
In certain cases, an X-ray examination the neck and head area might be needed to determine the size of pharyngeal tonsils and extent of its infection.
In certain other severe cases, a child might be required to undergo a sleep study to evaluate if the child is suffering from sleep apnea. The study monitors the brain and breathing activity of the child using electrodes by making the child is made to sleep overnight at the clinic. Although the whole procedure is painless, it could be challenging for children to sleep in an unfamiliar place.
Adenoiditis Treatment
The mode of treatment depends on the severity of the condition. If the adenoids are not infected, the doctor may wait to see if the adenoids would shrink by itself as and when the child ages.
In some cases, medications such as a nasal steroid may be required for shrinking enlarged adenoids. However, removal of tonsils may be suggested if the child suffers from frequent tonsil infections that could lead to infections of sinus cavities and ear despite medications. It is a simple procedure and doesn’t involve many risks. This surgery is also known as adenoidectomy.
Operative techniques include:
- Ablation
- Cauterization
- Curettage
- Laser therapy
- Adenoidectomy, following the administration of a topical or general anesthetic
Adenoiditis Post-Surgery Symptoms
After the removal of adenoids following things can be experienced by a child:
- A sore throat: Some children may experience a sore throat for a week to ten days and difficulty in eating and swallowing.
- Fever: Low-grade fever may be experienced even after several days of surgery. Precaution is needed if the fever exceeds 102 F and is shows other symptoms like stiff neck, lethargy, vomiting, or nausea, headache.
- Mouth breathing: Due to swelling of the throat after the surgery, a child can breathe through mouth and snoring may occur following the surgery. By 10 to 14 days following surgery, normal breathing resumes once swelling reduces. However, medical attention is needed if there is difficulty in breathing.
- Minor bleeding: Small spots of blood in the nose or in the saliva may be expected
- Scabs in the mouth: It normal for development of thick, white scabs at the region where the adenoids or tonsils are removed. Most scabs fall off naturally in small fragments within 10 days of surgery. The scabs are known to cause bad breath.
- Earaches: Some children can experience throat and ear aches for a few weeks following surgery. Medications for reducing pain may be suggested during this time.
- Blocked nose
Above mentioned symptoms should clear within a few weeks of surgery.
Adenoiditis Recovery Post Surgery
Following surgery, antibiotics are prescribed for protection against infections and mild pain relievers during the initial days for managing pain.
Following points help a child recover after surgery:
- Eating soft foods like soup, popsicles, Jell-O, and scrambled eggs
- Eating or drinking milk and milk products within the first 24 hours following surgery. After which, food like ice cream, yogurt, and pudding can be consumed.
- Avoiding warm foods for the first week after surgery
- Consuming cold and icy foods and drinks, such as milkshakes and ice creams
- Intake of a surplus of fluids in order to avoid dehydration
- Adequate rest should be provided within few weeks of surgery.
- Once a child can feed on regular foods, is no longer taking pain relievers and able to have a sound sleep throughout the night, the child can go to school
Adenoidectomy: Warning Sign
A child needs to be given immediate medical attention or rushed to the emergency room if bright red blood is noticed in mouth or nose as it may be an indication of scabs peeling off early. Also, medical care must be provided if there is difficulty in breathing accompanied by wheezing as it might a sign of excessive swelling of the surgical area.
It is advised to be well informed about surgery and must be well informed before opting for surgery. In case of doubts, a second opinion from another qualified clinician should be sought.
Adenoiditis Prevention
In order to prevent adenoiditis doctors recommend the following things:
- Consuming healthy foods and drinking plenty of liquids
- An adequate amount of sleep
- Following good hygiene practices can decrease infection chances
- Seeking timely medical help if the child shows symptoms of adenoiditis
Pharyngeal tonsil Pictures
Take a peek at these images of this tonsil to know how it appears to view.
Picture 1 – Pharyngeal tonsil
Picture 2 – Pharyngeal tonsil Image
References:
http://www.wisegeekhealth.com/what-is-a-pharyngeal-tonsil.htm
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Adenoid
http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/pharyngeal+tonsil

I appreciate your explanation and I need your help