What is an Abducens Nerve (CN 6)?
Also known as the sixth nerve, sixth cranial nerve, CN VI, the Abducens Nerve is a somatic efferent nerve in human anatomy. It helps in managing the movement of the lateral rectus muscle of the eye. The lateral rectus muscle helps in lateral gaze (the contraction of the eyes causes’ abduction)
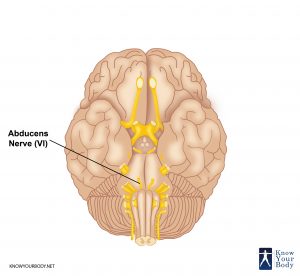
Abducens Nerve Location
The Abducens Nerve comes from the abducens nucleus in the pons (part of the brainstem). The nerve thereafter departs from the brainstem at the intersection of the medulla and pons.(located in the brainstem at the anterior to the cerebellum).
Before entering the orbit of the eye via the superior orbital fissure, the nerve first travels through the cavernous sinus at the tip of the petrous temporal bone. Inside the eye’s orbit, the Abducens Nerve then ceases by innervating the lateral rectus muscle. There are 4 divisions of Abducens Nerve:
1. cavernous sinus portion
2. orbital portion
3. nucleus and intraparenchymal portion
4. cisternal portion
Abducens Nerve Anatomy
1. Nucleus – Within the pons, the nucleus is situated at the upper part of the rhomboid fossa beneath the colliculus facialis.
2. Cisternal portion – These nerves emerge below the pons at the pontomedullary junction into the prepontine cistern. It then routes to the clivus and is enclosed within a fibrous casing called Dorello’s canal. The nerve then takes a turn towards the medial petrous apex towards the cavernous sinus.
3. Cavernous sinus portion – Inside the cavernous sinus, the Abducens Nerve is situated at the inferolateral in the internal carotid artery, medial to the lateral wall of the sinus.
4. Orbital portion – Once the nerve enters the orbit through the superior orbital fissure. It is an inferior nerve that passes through the tendinous ring.
Abducens Nerve Function
The Abducens Nerve also termed the sixth nerve is a somatic efferent nerve in human anatomy that helps in controlling the movement of the lateral rectus muscle (lateral side of the eyeball in the orbit) located in the eye area.
Abducens Nerve Related Conditions
The nature of damage and injury can be manifold in the long course of Abducens Nerve that is situated between the brainstem and the eye. It is susceptible to a number of clinical conditions such as:
- Abrasion to the brainstem can cause damage of eye by elongating it in between its point of origin at the pons where it is hung from the top of the petrous temporal bone.
- Damage to the peripheral part of the Abducens Nerve causes double vision or diplopia. A one-sided damage to the Abducens Nerve can cause incomplete abduction of the affected eye.
- Anything that can directly harm or stretch the nerve can cause a vulnerable damage. The peripheral sixth nerve damage can be caused by tumors or fractures, infections such as meningitis, demyelination, cavernous sinus diseases, and various other neuropathies such as the diabetic neuropathy.
- Some other rare causes of isolated sixth nerve damage include Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome which is caused by thiamine deficiency (in case of heavy alcoholism).
- A horizontal gaze palsy that affects both eyes simultaneously can cause damage to the abducens nucleus and does not produce isolated sixth nerve palsy causing the nuclear lesions. Abrasion of the abducens nucleus creates obvious sixth nerve problems, most notably internuclear ophthalmoplegia or the INO.
- Tuberculosis is another damage causing factor wherein 15 – 40 percent of the population suffering from this disease have some or the other cranial nerve deficit.
The Abducent nerve or the CN VI is tested by asking the patient to keep their heads still. The physician or the doctor then draws two large H formations in front of the patient. The patient is advised to follow the fingers that draw the letter H. While doing so if the patient feels any discomfort or double visions then the necessary course of therapy is advised.
Frequently Asked Questions
Are Tuberculosis and Abducens Nerve Palsy related?
Tuberculosis is a serious and a common infectious disease caused by the Mycobacterium tuberculosis organism. Tuberculosis and Abducens Nerve Palsy are a mediator to each other mostly in case of children. While in adults, 15-40% of people suffering from tuberculosis will have a resulting cranial nerve deficit mostly in the sixth nerve leading to Abducens Nerve Palsy.
What is diplopia?
Once the peripheral part of the Abducens Nerve is damaged it causes a double vision called diplopia. When affected, the patient’s eye is pulled towards to be looked at the outline. If there is a one-sided injury to the Abducens Nerve it causes a seizure in the eyes and diplopia becomes worst when a patient attempts to look laterally.

No comments yet.