Chordae tendineae Definition
These are string-like bands of fibrous tissue that attach to the cusps of the lower chamber of the heart. The structure is also known by the following names:
Heart strings
Tendinous chords
Chordae tendineae Origin
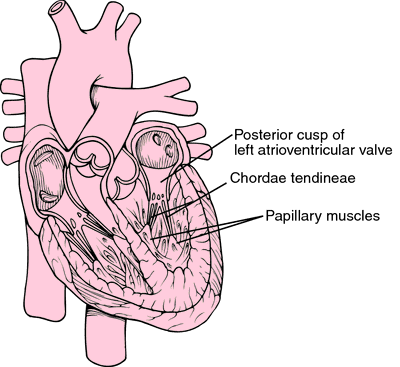
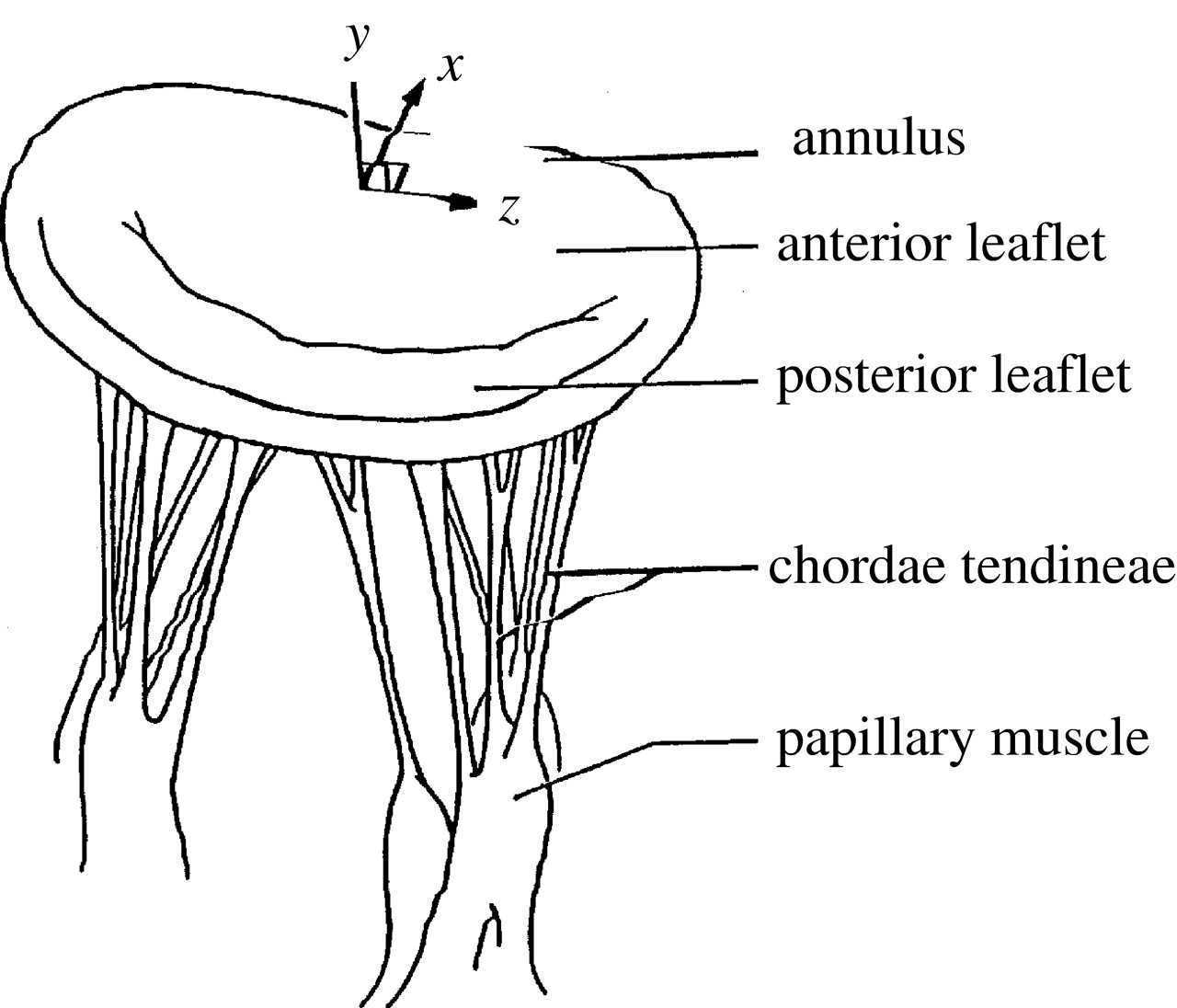
The cord-like tendons emerge from small stacks of muscle tissue called papillary muscles that inwardly project from the walls of the ventricle.
Chordae tendineae Location
These are situated between the edges of the tricuspid and mitral valve of the heart and on the other end of the papillary muscles.
Chordae tendineae Anatomy
These are made of a tough band of fibrous connective tissues that comprise of 80% collagen and 20% of elastin and endothelial cells. The collagenous strands along with the opening of the coronary sinus and the septal cusp of the tricuspid valve form the triangle of Koch with the tendon of Todaro. The flexible, inelastic cord is a lateral structure of the Eustachian Valve of the Inferior vena cava and the Thebesian valve of the coronary sinus. The atrioventricular node originates from the center of the Koch’s triangle.
Chordae tendineae Function
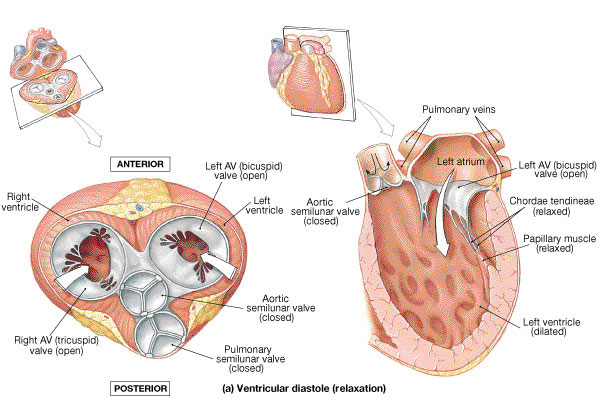
The strands of fibrous tissue shrink during atrial systole, an event when the atrium contract and blood flows from the auricles to the ventricles. On the other hand, in ventricular systole, the thick muscular walls of the ventricles contract as a result of high pressure than the arteries and close the atrioventricular valves. In this way, the blood is prevented from flowing back into the atria. A low-pressure gradient is simultaneously created when the blood passes into the ventricles from the atria. The tendinous chords pull the flaps or cusps of the valves and prevent them from swinging back into the upper chamber of the heart.
Chordae tendineae & Papillary muscles
Chordae tendineae and papillary muscles offer extreme support to the leaflets of the mitral and tricuspid valves. These keep the leaflets stable and thereby help in the prevention of blood from a backward flow. The valves have two leaflets along with three leaflets of the aortic and pulmonic valves.
Chordae tendineae Diseases
Degenerative cardiac disorders often cause the heart strings to rupture. This is more pronounced when the valves are severely affected. Ruptured tendons are most often attributed to the following conditions:
Rheumatic fever
Chest trauma
Connective tissue disorder
Valvular diseases
Ischemic heart disorder
Myocardial infarction
Chordae tendineae Pictures
References
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chordae_tendineae
http://www.innerbody.com/image_card02/musc31-new.html
http://news.rapgenius.com/Human-physiology-pulmonary-function-i-lyrics#note-1651433

No comments yet.