Cricoid cartilage Definition
The Cricoid cartilage is the ring-like formation at the base of the larynx. This structure also forms the uppermost part of the Trachea. The Cricoid cartilage is frequently referred to as the voice box and it forms the laryngeal prominence in men which is also known as Adam’s apple.
Cricoid cartilage Shape
The Cricoid cartilage has a circular ring-like structure. The word “Cricoid” is derived from the Greek term “krikoeides” which means “ring-shaped”.
Cricoid cartilage Composition
The Cricoid cartilage is made of yet another cartilage called Hyaline. Due to this reason, the Cricoid cartilage can undergo the process of calcification or ossification, especially during old age.
Cricoid cartilage Location
The Cricoid cartilage is located inferior to the thyroid cartilage situated in the neck.
Cricoid Cartilage Vertebral Level
In humans, this cartilage is located in the sixth level of the cervical vertebra.
Cricoid cartilage Surface Anatomy
The median cricothyroid ligament is joined to the Cricoid cartilage medially and the cricothyroid joints are attached to it postero-laterally. Below it around the trachea are located the rings of cartilage. These rings are C-shaped and are not continuous; they have a gap between them. This C-shape and gap enables the food to pass through the esophagus. The cricotracheal ligament joins the Cricoid to the first tracheal ring.
The posterior signet part of the Cricoid is known as the lamina. It is comparatively a bit broader than the anterior and lateral parts of the Cricoid cartilage. The anterior band part is known as the arch.
The Cricoid cartilage can be said to be the only complete cartilage of the larynx.
It forms an important part of the laryngeal structure. It provides us with attachments for the ligaments and muscles which coordinate the glottis.
Cricoid cartilage forms one of the six laryngeal cartilage types. The other five of them are as follows:
- Epiglottis: Attached to the thyroid gland, Epiglottis is composed of fibrocartilage with a spoon-like shape. It does not get paired up with the cricoids cartilage.
- Thyroid: It is Adam’s apple of the human body, which consists of two hyaline laminae.
- Corniculate: It is a aired cartilage that is found at the top of the arytenoids cartilage.
- Arytenoid: It is triangular cartilage that appears in pair ad surrounds the cricoids cartilage.
- Cuneiform: This is the paired cartilage that has no articulations and is found on aryepiglottic folds.
Cricoid cartilage Function
The basic function of the Cricoid cartilage is to connect various ligaments, cartilages, and muscles which are involved in closing and opening of the airways as well as in the production of speech. The Cricoid cartilage is a very strong connective tissue which forms a sheath over the ends of the bone joints. It provides a surface for articulation and provides smoothness and flexibility of the joints.
In cases of severe respiratory problems when other procedures fail to improve the respiratory conditions of the patient, a hollow needle is inserted into the cartilage to help the patient in breathing. This procedure is known as Emergency Airway Puncture or Cricothyrotomy.
Cricoid Cartilage Clinical Significance
Cricothyrotomy
In case of blockage or improper establishment of an airway, cricothyrotomy may be performed in an emergency. Through this, respiration could be provided to patients by accessing their trachea. During the examination, cricothyroid membrane needs to be identified first. For this, you need to track the location of the thyroid notch and the cricoids cartilage as the membrane is present in between them.
As soon as the identification is properly done, an incision is made on the cricothyroid membrane. A tube is immediately placed in order to keep the membrane open after incision. This way, the airway can be established and the person’s life is saved. In a few cases, patients have a pyramidal lobe that comes out of the thyroid gland. Due to this, the cricothyrotomy region is occluded. In this situation, if the lobe is cut, the patient may suffer from severe haemorrhage.
Laryngeal Cartilage Fracture
One of the most frequent and very common problems with the cricoid cartilage is the fracture of laryngeal cartilages. The ones that are mostly fractured include thyroid and cricoids cartilages. Physical injury or trauma is the main reason behind these types of fractures. In the fracture scenario, the patient develops laryngeal swelling, inflammation, and haemorrhage. The fracture may lead to speech issues and airway obstruction.
When prior to surgery the anesthesiologist intubates a patient under general anaesthesia, he or she will exert a pressure on the Cricoid cartilage in order to compress the esophagus lying behind the cartilage and thereby preventing any gastric influx from occurring. This procedure is known as Sellick manoeuvre.
For several years, The Sellick manoeuvre was accepted as the standard procedure to be followed during Rapid Sequence Induction. Even now the American Heart Association recommends this method of pressuring and squeezing the Cricoid while resuscitating using a BVM as well as while handling Emergent Oral Endotracheal Intubation. However, recent research in this area strongly indicates that this method of applying pressure on the Cricoid may not be as good as once it was thought.
The procedure can at times prove to be very harmful as the Cricoid pressure may be often applied in a wrong way. Cricoid pressure when wrongly applied may laterally move the esophagus instead of compressing it, which is the prime objective of Sellick Maneuver. There are many studies which demonstrate that this can compress the glottis and result in increased peak pressures and lowered tidal volume. The current literature indicating these findings have been instrumental to make this once widespread practice almost obsolete.
Sometimes blockages may be formed within the trachea. This may happen due to the calcification of the Hyaline cartilage which blocks the windpipe. Patients of increasingly old age may suffer from such causes. This may cause inflammations and pain of the Cricoid cartilage. A medical operation known as Cricoidectomy may be performed in such cases to relieve the patient from such blockages. In this procedure, the Cricoid cartilage is removed partially or completely, as the individual case may need.
Cricoid Cartilage Pictures
Here are some pictures which will show you the location of the Cricoid cartilage in the human body and how does it appear externally.
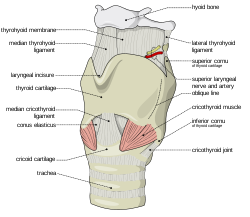
Picture 2 – Cricoid cartilage Image
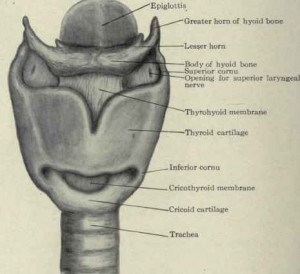
Picture 3 – Cricoid cartilage Photo

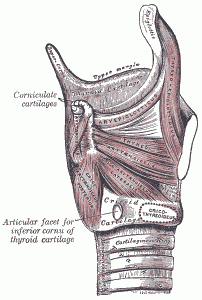
No comments yet.