What is Endosteum?
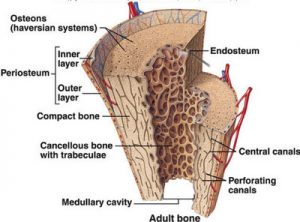
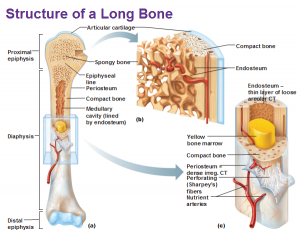
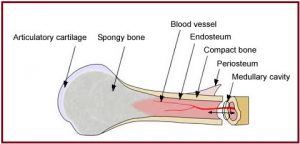
Endosteum is a thin, soft, connective tissue, lining the cavity of long bones like Humerus and Femur. It acts as a coating for the inner compact bone and the trabeculae of the spongy tissue. The osteoprogenitor cells of the preosteoblasts present in this connective tissue lining, differentiate into osteoblasts and later on to osteocytes, which are the bone forming cells. They also aid in the formation of bone-matrix secreting cells, also known as bone-lining cells. The endosteum, along with the periosteum functions for the growth of bone in diameter. Endosteum also contains Haematopoietic Stem Cells or HSCs which are totipotent in nature and play a role in the production of all types of blood cells.
The endosteum is also medically termed as the medullary membrane, located in the diaphysis (cavity of long bones). The cavity of long bones consists of red and yellow bone marrow lined with spongy tissue and cancellous bones.
Where is the Endosteum located?
The endosteum can be seen in the T.S. of any long bone. This layer of membrane envelopes the spongy tissue, the medullary cavity and the internal lining of the bone’s cavity and the Haversian canal of the marrow. Endosteum is located in bones such as femur, humerus, hip bone, thoracic rib bones and sesamoid bones like patella. It is also seen lining many walls of different sinuses of the skull.
What are the different types of endosteum?
Depending on the inner bone area where it is found, mainly 3 types of endosteum are known:
- Cortical endosteum: The cortical endosteum found on the inner walls of cortical bone acts as the border of the marrow cavity. This cavity stores the yellow bone marrow, which is a reserve of fat cells or adipose cells. During severe starvation and malnutrition, these fat cells are utilized as fuel to produce energy for vital functions of the body. This, in turn, would reduce the thickness and density of the bone. Hence, the cortical thickness of the bone reduces producing a harmful effect on vital functions like storage and release of calcium. Since cortical weight contributes to 80% of the body’s entire weight, the patient is seen to experience weight loss.
- Osteonal endosteum: Located on the inner walls of the osteonal canal, present in compact bones, this endosteum contains the nervous and vascular supply of the bone.
- Trabecular endosteum: This endosteum lines the inner walls of the trabeculae, that is, the bony parts covering the spongy tissue of bone near the shaft. It aids in absorption and reduction of bone damage caused due to an impact. This part of the bone contains the red bone marrow containing Haemopoietic cells capable of neo-erythropoiesis (production of new RBCs).
What is the clinical importance of endosteum?
Exchange of factors such as blood cells and calcium between bone marrow and blood vessels takes place through the osteoblasts of the endosteum called the Endosteal Cells. These cells are active participants in bone growth, repair, and remodeling. Endosteum and periosteum together contribute to bone repair and reconstruction after a fracture. The cells of both the layers are capable of undergoing rapid mitosis and proliferation after which, they migrated towards the site of bone injury.
In certain cases, medullary lesions can be observed along the inner aspect of the cortical bone, leading to endosteal scalloping which may come up to be associated with both benign as well as malignant forms of tumors. These can also lead to skeletal metastasis in acute stages.
What are the Functions of Endosteum?
Endosteum has several important functions in the body, as it forms a part of the long bones of the human body. Some of its major functions are as follows.
1. Appositional Bone Growth
- Osteoblasts lining the endosteum secrete bone matrix and form ridges alongside the periosteal blood vessels.
- The bony ridges enlarge and meet to convert the groove into a tunnel containing the blood vessels.
- The periosteum lining the tunnel transforms itself into endosteum and hence, the osteoblasts lining the tunnel start secreting the matrix, making the canal narrow.
- Osteoblasts under the endosteum form new lamellae and a new osteon is formed.
- In the end, a new circumferential lamella elaborates beneath the periosteum and the process is repeated for continuous enlargement of bone diameter.
- This is mainly observed in children as a fast-paced process, which slows down considerably once adulthood is attained.
2. Bone Repair
During a traumatic injury or a fracture, the occurrence of a hematoma within the bone causes rapid multiplication of the endosteal cells to reestablish a bridge of reparatory callus and aid in bone solidification.
3. Bone Remodelling
The endosteum stimulates bone resorption at the inner surface of the bone along with periosteum that stimulates the continuous formation of new bone from the outside. This leads to increase in the diameter of both, medullary canal as well as the bone as a whole.
Endosteum Pictures
What is the difference between endosteum and periosteum?
There are a number of differences between the two linings, endosteum, and periosteum. Some of them are listed below:
- Endosteum is located in the medullary canal, spongy tissue of bone, Volkmann’s canal, and the Haversian canal while the periosteum is situated on the outer bone surface of all bones, except sesamoid bones.
- Endosteum is made up of a single-celled layer and s a loose connective tissue, whereas, the periosteum is bilayered in itself, having a fibrous and a cellular layer called cambium and is a dense and irregular connective tissue.
- Endosteum thickness is in the range of approximately 10 micrometers, while that of the peritoneum is about 0.1-0.5mm.
- Endosteum mainly aids in bone growth, repair and remodeling whereas, periosteum aids bone sensitivity and nourishment along with the above activities.

No comments yet.