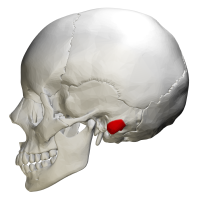
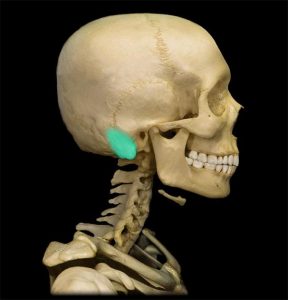
Mastoid Process Definition
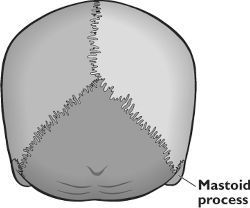
The human skull is made up of many bones held together by fibrous joints called sutures. The inferior surface houses a number of processes for strong attachment of various structures of the face and neck region. The mastoid process, lying in the mastoid part of the temporal bone in the human skull, is a conical/pyramidal projection present each side of the head, at the base of the skull. It is the prominent bony protrusion easily seen behind the earlobes.
Mastoid Process Location
The mastoid process is located behind the external auditory meatus, lying lateral to the styloid process, at the vertebral level of C1.
Mastoid Process Anatomy
The mastoid process is a pair of conical bones projecting downwards, arising from the posterior ends of the parietal bones of the skull. The parietal bones are a pair of bones present on each of the lateral walls of the skull, encompassing the middle and the inner ear. The posterior border shows articulation with the occipital bone, while the anterior border is merged indistinctly to the descending portion of the visually flat section of the temporal bone. The petrosquamous suture can be seen running vertically above the process.
Mastoid Process Functions
- Its rough outer surface provides anchorage to the occipitofrontalis muscles which cover the skull from the cheek bone to the process. This muscular covering is innervated by the posterior auricular branch arising from the facial nerve (Cranial Nerve VII).
- The mastoid process gives rise to a number of muscles namely,
- sternocleidomastoid muscle, responsible for the contralateral rotation of the head;
- splenius capitis muscle, responsible for rotatory flexes of the head;
- posterior belly of gastric muscles, responsible for the opening of jaw and
- longissimus capitis muscle, responsible for one-sided rotatory reflex of the head.
- The medial portion of the process consists of a deep groove named digastric fossa, allowing digastric muscles to anchor.
- The mastoid air cells or Lenoirs are the hollow spaces present in specific areas of the process, which can be prone to infection and inflammation. These cells connect to the middle ear and are covered by the mucoperitonial membrane, which is a continuation of the tympanic cavity and the squamous section of the temporal lobe.
- The process also houses a shallow occipital groove protecting the occipital artery.
- The presence of enlarged muscles of the human male body, the mastoid process in males can be seen more prominently which, in certain instances can help in forensic findings of the gender of an unidentified body.
- The mastoid process is not prominent at the of birth as the process only enlarges the muscles responsible for head and neck movement develop till the child is 2 years old.
Mastoid Process Pictures
Medical Ailments With Respect To The Mastoid Process
Mastoiditis
It is referred to as inflammation and infection of the mastoid bone. In infants, it can be a prominent cause of mortality as it is hard for the medication to reach the target.
1. Causes -The main cause of mastoiditis is otitis media. The Lenoir cells gain infection as they are in close contact with the middle ear.
2. Signs and Symptoms –
- Pain in ear,
- Fluid drainage from external ear,
- Enlarged ear,
- Swelling and redness around the process,
- Impaired hearing,
- A headache and fever.
3. Treatment –
- Antibiotics, ear drops, and ear cleaning may be suggested.
- Myringotomy, fluid drainage from the ear
- Mastoidectomy, removal of the infected mastoid bone through surgery.
If left untreated, Mastoiditis may lead to permanent hearing loss, meningitis, brain abscess, and lesions which can be fatal.
Mumps
Infection in the parotid glands causing severe pain which aggravates during chewing causes severe pain as the sheath protecting the parotid gland limits the swelling of the gland.when the mouth is opened for chewing, the swollen parotid gland moves back and irritates the facial muscles thereby compressing e mastoid process, causing pain.
Cholesteatoma
It is an ear disease where a cyst starts forming below the mastoid process owing to the incomplete opening of the Eustachian tube for equalizing air pressure in the pharynx. It can lead to chronic ear infection and hearing impairment if not treated on time. Treatment includes surgical processes followed by appropriate medication to help prevent recurrence of the cyst.
Mastoid Cancer
The formation of malignant tumors due to abnormally growing squamous cells, the mastoid tumor is a form of skin cancer.

No comments yet.