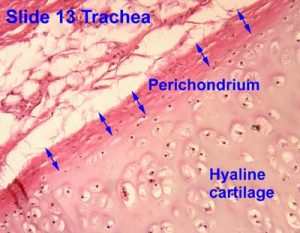
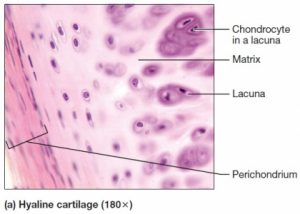
The perichondrium refers to a dense membrane of connective tissue that covers cartilage in different parts of the body except for the cartilage in joints.
It is a dense tissue but it is porous and fibrous and wraps around the cartilage. The high density of this connective tissue is found in infants and young children.
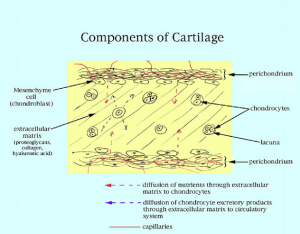
Layers of the Perichondrium
The perichondrium has two layers:
Outer layer – The outer layer is fibrous in nature and is made of dense connective tissue. It contains fibroblasts which secrete collagen.
Inner layer – The inner layer of the perichondrium is chondrogenic in nature and can proliferate and turn to form chondroblasts.
Functions of the Perichondrium
- The perichondrium protects growing and developing bones against any trauma or injury. It is basically a protective membrane and in case an injury does occur, it promotes cellular regeneration which helps in fast recovery.
- The perichondrium is both fibrous and porous in nature. Because of this, blood flow is easily facilitated. It helps transport oxygen from one part of the body to another.
- Apart from this, nutrients are also supplied to the different parts of the body. This helps nourish the cartilage and keeps it strong and healthy.
- The perichondrium provides elasticity to the parts of the body by reducing friction during movement.
Location of the Perichondrium
The perichondrium is found throughout the body but it is mostly concentrated in parts like the ears or the nose that protrude out. The perichondrium covers hyaline cartilage found in the trachea of the throat, the larynx or voice box, the epiglottis, the region where ribs connect to the sternum and between vertebrae of the spine.
It is however absent in articular cartilage found in joints and where tendons and ligaments attach to bones.
In children, the perichondrium is found even in articular cartilage in joints but not in adults. Therefore, growth and repair of the cartilage through cellular regeneration tends to be better in children but poorer in adults.
Difference between Perichondrium and Periosteum
The periosteum is another layer of connective tissue. Its function is similar to the perichondrium in terms of protection. But the main difference between the two layers has to do with nutrition. The blood vessels of the perichondrium can deliver nutrients to cartilage but not to the bones. The periosteum, however, can deliver nutrients to the bones as it produces osteoblasts.
Disorders of the Perichondrium
- Cauliflower ear– this is a common condition found in athletes, especially boxers where they receive a hard blow to the ear. It damages the perichondrium and blood flow to the inner tissues of the ear is affected resulting in a part of the ear resembling a cauliflower. The doctor can treat this by removing the blockage so that blood can flow through easily to the tissues. Stitches may be needed and antibiotics are also often prescribed.
- Perichondritis – This occurs when the perichondrium gets inflamed and may get infected due to trauma to the part or insect bites or piercings. This can be treated with antibiotics and if there is an abscess formed, it can be drained and treated.
Perichondrial Grafting
Perichondrial grafting is done usually when there has been some heavy injury or intense trauma to the cartilage. Surgery of the perichondrium is usually done to replace the tissues in the nose (through rhinoplasty) and also for repairing the eardrum in case of injury.
Perichondrium Pictures
The perichondrium is a dense membrane of connective tissue that protects the cartilage of the body except in joints. It helps supply nutrients and oxygen to different parts, thereby nourishing and supporting the cartilage.
References
http://www.medicinenet.com/script/main/art.asp?articlekey=7896
http://www.wisegeek.com/what-is-the-perichondrium.htm
http://medical-dictionary.thefreedictionary.com/perichondrium
http://www.webmd.com/skin-problems-and-treatments/cauliflower-ear-symptoms-causes-treatments
http://www.nytimes.com/health/guides/disease/perichondritis/overview.html?mcubz=0

No comments yet.