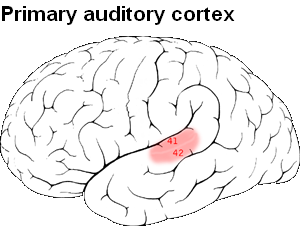
What is the Primary auditory cortex?
It is that region of the brain which dispenses sound and is responsible for the ability to hear. It is an essential section of the cerebral cortex which accepts auditory data from the medial geniculate body. It is the primary cortical area of the auditory passageway.
This brain region is also referred to as “Auditory Area”.
Primary auditory cortex Location
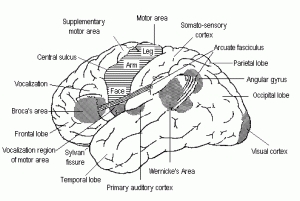
It is situated in the temporal lobe (on the superior temporal gyrus), which is located right above the ears. It receives each and every data from the ventral dissection of the medial geniculate complex.
Primary auditory cortex Function
The Auditory Area is a significant part of the hearing process. Its primary function is to process sound along with its volume and pitch. The location of the sound is also processed via primary auditory cortex. This auditory cortex is essential to comprehend the spoken language and is concerned with tasks such as finding out and separating the auditory objects.
Primary auditory cortex Damage
Any kind of severe damage to the primary auditory cortex of the nervous system may lead to complete loss of hearing. Such an individual may not be aware of the different kinds of sounds in the surroundings. However, the ability to automatically respond to sound would still persist. This is due to the reason that both the ears are connected to the left and right auditory cortex. Thus, a person who has experienced a wound on one part of the auditory cortex can classify the different sound frequencies conveniently.
Primary auditory cortex Development
Unlike the visual system, the auditory system develops at a much faster rate; although it may take few years for such complicated nervous functions to become fully functional. Infants, however, find it much complicated to differentiate between low and high sound frequency. In adults, the sensitivity to high frequency develops at a much faster rate.
Primary auditory cortex Brodmann areas
Brodmann areas 41 and 42 are included in auditory processing and serve as one of the essential components of the nervous system.
Brodmann area
It is also known as anterior transverse temporal area 41 and is a part of the cytoarchitecturally stated temporal areas of the cerebral cortex.
Brodmann area 42
It is referred as posterior transverse temporal area 42 and is also one of the significant cytoarchitecturally defined temporal areas of the brain cortex.
Primary Auditory Cortex Clinical Significance
Acoustic Analyzer
A primary auditory cortex acts as an acoustic analyzer, a traditional model depicts. The organ helps in responding selectively to various physical parameters of sound, which is indicated through the sound level, sound frequency, amplitude, and other factors. It is this coordination between acoustic parameters and cellular responses that offer a competitive platform to auditory neuroscience. Whether it is the auditory cortex or the subcortical auditory system, the coordination helps in the proper understanding of the neural bases that lead to the hearing.
Learning and Memory
The primary auditory cortex plays a vital role in the learning and memorizing processes. According to the studies conducted, it was observed that the cortical responses increased when the sound waves indicated a reward or punishment.
Primary Auditory Cortex Pictures
Take a look at these images of Primary Auditory Cortex to know about its physical appearance.
Picture 1 – Primary auditory cortex
Picture 2 – Primary auditory cortex Image
References:
http://www.answers.com/topic/auditory-cortex
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Primary_auditory_cortex
http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK10900/
http://www.livestrong.com/article/165212-primary-auditory-cortex-functions/

No comments yet.