Sural nerve Definition
It is a sensory nerve in the lower leg that lies close to the small saphenous vein, situated in the calf. As the bundle of fibers forms a branch of the femoral nerve, it is also known as “short saphenous nerve”.
Sural nerve Origin
The nerve normally emerges from the junction of the medial sural cutaneous with the peroneal anastomotic branch of the lateral sural cutaneous nerve.
Sural nerve Location
It is specifically located in the lower lateral leg and lateral aspect of the foot.
Sural nerve Innervation
It innervates the muscles of the lateral and posterior third of leg as well as the lateral aspect of foot and heel.
Sural nerve Anatomy
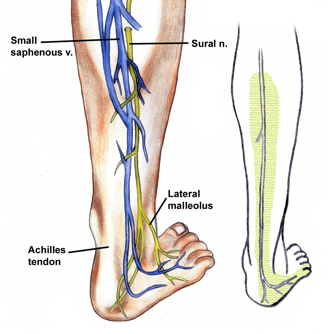
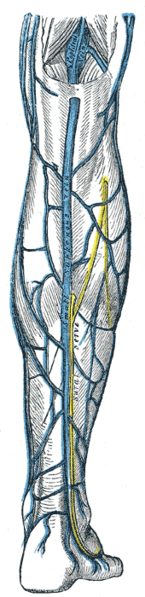
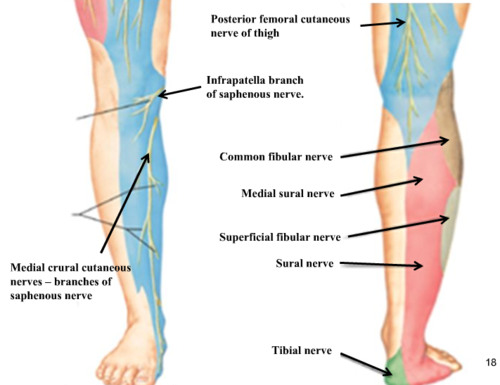
As aforesaid, it is purely a sensory nerve and does not consist of motor fibers. The short saphenous nerve initially courses posterior between the heads of the gastrocnemius muscle. It runs down and passes near the lateral margin of the Achilles tendon, which is present in the tendon of the posterior leg and lies with the small saphenous vein. Later, it enters the gap between the lateral malleolus and the calcaneus. It continues as the lateral dorsal cutaneous nerve below the lateral malleolus and joins the intermediate dorsal cutaneous nerve on the dorsum of the foot. The terminal branches of the nerve communicate with the collateral branches off of the common tibial and fibular nerve. It comprises of spinal nerve roots from S1 and S2. It acts as a guide to the tibial nerve since it lies superficial to deep fascia below the knee. It is in close approximation with the peroneus brevis tendon. Distribution of the cutaneous nerves is clearly visible on the sole of the foot when examined closely.
Sural nerve – Insertion
Between its movement down the popliteal fossa and underneath the gastrocnemius, sural nerve produces a cutaneous branch known as the medial sural cutaneous nerve. This nerve moves laterally upward to the lateral head of gastrocnemius. The common fibular nerve simultaneously leads to the development of a small cutaneous branch, which is called the lateral sural cutaneous nerve. The branches during their ending phase move on the dorsolateral side of the little toe and proceed to the lateral part of the foot.
This lateral sural cutaneous nerve then proceeds to the superficial fascia posterior portion of the foot and forwards to the lateral malleolus close to the short saphenous vein, moving down to the gastrocnemius muscle’s belly through the deep fascia between the legs. This is the position where it joins the sural connecting branch coming from the common fibular nerve.
Sural nerve Function
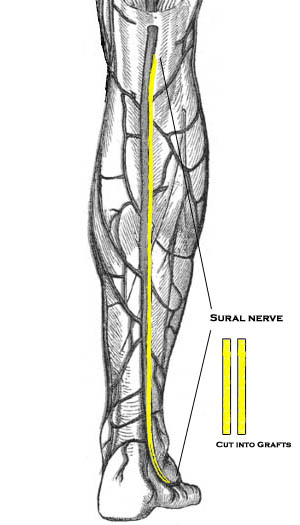
It mainly supplies the branches to the skin on the back of the leg before continuing as the cutaneous nerve along the outside of the foot and little toe. Most importantly, the nerve is used to relay sensory information about the lower calf and external foot to the brain. Since the short saphenous nerve is in close proximity to the skin, it finds greater use in nerve biopsy. In this procedure, a 3-5cm section of the nerve is harvested at the level of the ankle. Microscopic evaluation of the sample may provide some clues to diseases like demyelination, sarcoidosis, amyloidosis, and leprosy. It is also a common source of nerve cable graft material. Here, a piece of the donor nerve is excised and transplanted to the area of neurological damage in order to restore muscle function, particularly in the case of damaged limbs and ulnar nerve injury. Patients with sexual dysfunction post prostate cancer surgery often undergo sural nerve transplantation to regain the normal libido. However, there are no specific CPT codes for nerve grafting. It is also required for nerve conduction studies to detect demyelination. Doctors often use the median superficial sural artery and nerve to create a flap for correcting anomalies around the foot as well as the ankle. Innumerable studies have been globally conducted to further analyze the anatomical variations of the nerve. In many surgical interventions, the nerve is often blocked to carry out the required procedure smoothly. These may include:
- Ankle block to correct a fractured/dislocated ankle
- Elimination of a foreign material in the lateral posterior calf
- Repair of wounds
Clinical Relevance
Sural Nerve Block
A sural nerve block is used for making the effect of anesthesia on the foot as well as lower leg faster. Being superficial, this nerve is easily identifiable and accessible by surgeons.
Sural nerve Diseases
Severe trauma can often result in sural neuropathy, a common neurological problem caused due to a damaged nerve. It is a debilitating disorder that manifests into pain, and may cause numbness and tingling. This may eventually manifest into nerve palsy, which is evident during Tinel’s test. Some of its causes include:
- Ankle sprain/fracture
- Knee surgery
- Vein stripping
- Diabetes
- Ganglion cyst
- Vasculitis
Similarly, certain physiological abnormalities can lead to nerve entrapment/compression due to direct pressure on the short saphenous nerve, and produce symptoms akin to neuropathy. As the pathway of the nerve includes the fibrous arcade, it is the most common site for nerve impingement. In most cases, the left nerve is highly affected. Reduction of frictional irritation in this region with myofascial or active release is the only treatment available for this ailment. However, certain mobilization techniques such as neural flossing and nerve gliding exercises can ameliorate the painful symptoms to some extent since these methods involve regular stretching of the affected nerve. Irritation or injury to the nerve is known to cause sural neuritis/neuralgia, a bothersome condition marked by a burning pain in the lower leg, particularly in the heels. For the same reason, the tissues surrounding the sensory nerve can enlarge or swell and cause neuroma. Ablation of the nerve may help in reducing the pain. Some individuals may even develop focal lesions in the short saphenous nerve, which can be easily diagnosed by MRI scan and ultrasound imaging. In few instances, the nerve could get severely affected during varicose vein surgery.
Sural nerve Pictures
References
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/
http://www.innerbody.com/
http://functionalanatomyblog.

Thanks for enlightened write – up on Sural Nerve.
My query is : What is cause of absent of Sural Nerve ? Is it curable ? If yes, then what
is the treatment ? Where it can be available ? Is it associated with Peripheral Neuropathy ?where the treatment is available? Kindle name atleast five(05) best Neurological hospitals of the country