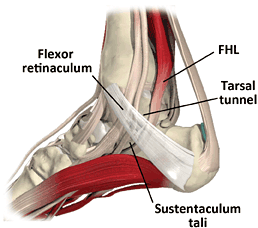
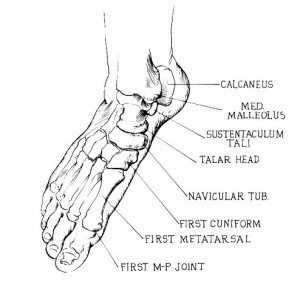
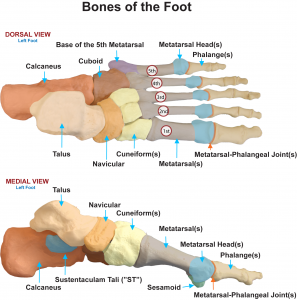
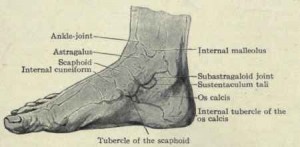
Sustentaculum Tali Definition
It refers to a horizontal shelf which arises from the anteromedial portion of the heel bone or calcaneus. The superior surface of the tali is bowl-shaped and communicates with the middle calcaneal surface of the talus. The inner surface has a channel for the tendon of flexor hallucis longus.
This structure is also known as Talar Shelf.
Sustentaculum Tali Location
It is present on the medial side of the calcaneus. This portion of the heel bone shows a prominent and console-shaped protrusion supported on the medial surface of the calcaneus. The Tali supports the thalus, another part of the heel bone. Its exact location is just above the calcanean ditch.
Sustentaculum Tali Etymology
The name is derived from a Latin word-sustenus which means to support. Tali refer to the talus bone present in the body. The other names of the Sustentaculum Tali are Small Apophysis of the Calcaneus or Astragalus Console.
Sustentaculum Tali Anatomy
The Talar Shelf is associated with several ligamentous structures namely:
- Deltoid Ligament (Medial Surface)
- Plantar Calcaneonavicular Ligament (Anterior Surface)
- Medial Talocalcaneal Ligament
This structure is also known as Talar Shelf. The upper side of this console-shaped protrusion (also the Sustentaculum Tali), which is known as dorsal supports the middle surface of the calcaneus. This part corresponds to the mid-calcareal surface of the talus bone in order to offer support to the talus.
The lower part of the Sustentaculum Tali supports the tendonus muscular flexoris hallucis longi wherein the tendon of the heel’s long flexor muscles merges.
Sustentaculum Tali Function
It is viewed as a weight-bearing carcass, essential for locomotion and to stand upright, however it is also vulnerable to injury. It sustains the interior of talus and prevents the ankle from sloping inward when the weight is put on the foot. Hence, it serves to maintain the center of gravity of the human body.
Sustentaculum Tali Pathology
This structure is involved in a number of medical cases of tarsal coalition, subtalar coalition and specifically talocalcaneal coalition.
Sustentaculum Tali Fracture
Fracture is typically caused due to an intense trauma or an accident. A direct medical approach is recommended in such cases. Fractures, where there are depressions of the medial facet, can be repaired or alternatively condensed percutaneously.
A Sustentaculum Tali fracture is divided into two types:
- Intra-articular fracture: This includes the calcaneo-cuboid joints and the subtalar joints.
- Extra-articular: This does not include the calcaneo-cuboid joints and the subtalar joints.
Sustentaculum Tali Fracture- Symptoms
The symptoms related to extra-articular fractures are not severe and so the symptoms are mostly not visible or felt. On the other hand, the symptoms of intra-articular fractures are more severe and they are:
- Patients tend to walk on the toe as they cannot walk properly on their heels.
- Rapid swelling and excruciating pain in the heel post-injury.
- It involves other associated fractures in the backside and other bones surrounding the lower limb.
- Due to leakage of blood seeping in other parts of the heel bone area, patients may notice reddish discolouration of the skin and sole of the heel.
Sustentaculum Tali Fracture- Diagnosis
The diagnosis of any SustentaculumTali fracture is revealed through X-rays. Several pictures are taken of the foot from different angles and positions. Doctors take X-rays of the other foot as well to compare the differences in the Bohler angle of the feet. CT scans are also done to get a clearer evaluation of the fracture.
Sustentaculum Tali Fracture- Treatment
Before visiting the doctors, there are a few initial treatments that are conducted for calcaneus fractures (both intra and extra-articular). These treatments include:
- Keeping the foot elevated as much as possible
- Absolute bed rest
- Intake of anti-inflammatory medicines to minimize swelling and pain
- Application of ice to reduce swelling
Once the aforementioned basic treatments start, doctors recommend more advanced treatments on the basis of the fractures. These involve:
- Once the swelling reduces and pain decreases, the patient is advised to do exercises for Type 1 fracture and undisplaced Type 2 and Type 3 fractures. Patients are strictly restricted from walking on their heels for at least 6 weeks.
- For any kind of displaced Type 2 and Type 3 fractures, the condition is treated with surgeries for realigning the fractured fragments that are held by screws and plates.
- For type 4 fractures, attempts are made to align the fragments by manipulation. A similar treatment technique is followed like the Type 1 fracture. Although a perfect anatomical structure of the fractured foot is not attained as it was before, doctors try to help patients become mobile as much as possible.
Calcaneus fractures may bear a deep impact on your mobility. In particularly, intra-articular fractures accelerate chances of arthritis in the future. This is because the joint can become incongruous leading to interruption in smooth mobility. It is, therefore, advised to follow the doctor’s advice at every step for better recovery.

No comments yet.