Adductor Magnus Definition
The Large triangular muscle in the medial side of the thigh is known as ‘Adductor Magnus’. As it is an adductor, it pulls and contracts the hip towards the body midline. This action enables activities like walking, running and a number of other actions. Though the adductor is a muscle, it is also considered a part of the hamstring group as well.
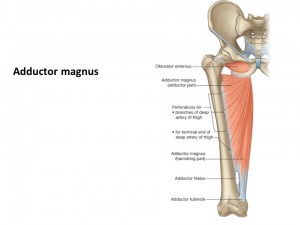
Adductor Magnus Location
Origin of the Adductor Magnus
The adductor magnus originates in the pelvic region, arising from the tuberosity and pubis of the ischium, which is also known as the sitting bones or sitz.
Different portions of the Adductor Magnus:-
- Pubofemoral or the Adductor portion– These fibers arising from the Ramus of the pubis are short, horizontal and are inserted into the rough line of the femur (thigh bone) leading from the greater trochanter (part of the femur) to the linea aspera (posterior surface of the femur, to which the muscles and intermuscular septum is attached), medial to the gluteus maximus.
- Ischiocondylar or the hamstring portion– The middle portion of the muscle, composed principally of the fibers coming from the tuberosity of the ischium, makes a thick, fleshy mass consisting of rough textured bundles, which move down vertically, ending about the lower portion of the thigh in a tendon, which is inserted to the adductor tubercle on the femur, which is connected by a fibrous extension to the line leading upward from the tubercle to the linea aspera.
Innervation Of The Adductor Magnus
It is a composite or hybrid muscle as the hamstring and adductor parts of this muscle are innervated by two different nerves. The hamstring part is innervated by the tibial nerve while the adductor portion is innervated by the posterior division obturator nerve.
- Adductor Head: Obturator Nerve
- Hamstring Head: Sciatic Nerve
Adductor Magnus Function
The main function of the Adductor Magnus is the adduction of the hip joint. It further supports outward rotation, inward rotation, flexion, and extension. Overall, the hip adductors play an important role in balancing the pelvis during daily activities like standing and walking. The adductor magnus brings the legs toward the midline of the body. These adductors are also responsible for adducting or crossing the legs across the midline of the body. Activities like basketball, football, ice hockey etc are made possible because of this muscle.
The lateral, upper part of the adductor magnus is an incompletely separated, often considered another muscle i.e, the adductor minimus. These are generally separated by a branch of the superior perforating branch of the profunda femoris artery.
Adductor Magnus Pictures
Check out some of the pictures of Adductor magnus muscle.

Adductor Magnus Image
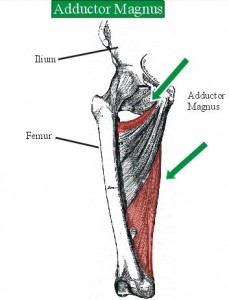
Adductor Magnus
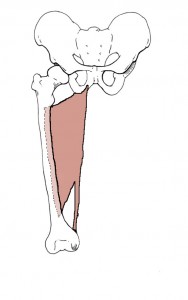
Adductor Magnus Picture
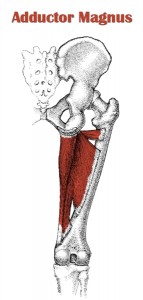
Adductor Magnus
Adductor Muscle Injuries
Adductor muscle strain usually involves inflammation and pain along the inner thigh muscles, which include the adductor longus, the adductor medius, the adductor Magnus, the gracilis muscle and the groin. The muscles attach to the bone via tendon. These muscles permit hip and legs to move across the body. Most of the injuries occur at the junction between the tendon and the muscle, or the attachment of the tendon to the pelvic bone. This strain may or may not be a complete tear of any muscle. Of these muscles, the adductor longus is the most commonly injured muscle.
The muscle strain is generally graded in three, namely, Grade 1, Grade 2 and Grade 3. A Grade 1 strain is mild in nature. there is no major tear, the tear being microscopic. There is no loss of strength. Whereas, the Grade 2 strain is moderate in nature. There is tearing of fibers within the substance of the tendon right at the junction of the bone and tendon or the muscle and tendon junction. There is a decrease in strength. The third Grade is where there is a complete rupture of the tendon, though this is highly uncommon.
SYMPTOMS
- There is a sudden pop in the inner thigh or the groin area at the time of the injury.
- Pain, swelling, warmth, redness, and redness which is further worsened by moving the hip and weakness of the hip.
- Bruising in the groin and inner thigh 48 hours following the injury.
- Spasms in the muscle in the groin and inner thigh.
CAUSES
- Prolonged overuse or sudden increase in the amount of intensity of an activity or the overuse of the inner thigh.
- Added force to the inner thigh
- Violent blow to the inner thigh
- Stressful overactivity
PREVENTIVE MEASURES
- Warming up before any sporting activity
- maintaining appropriate conditioning
- Proper sports technique
- Completing the full course of rehabilitation after an injury before returning to a sport.
References
http://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/adductor-magnus-muscle
http://www.healthline.com/human-body-maps/adductor-magnus-muscle
http://www.painrehabcenter.com/view.php?SC=3

No comments yet.