What is Quadratus Lumborum?
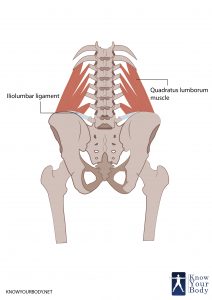
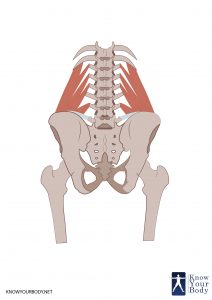
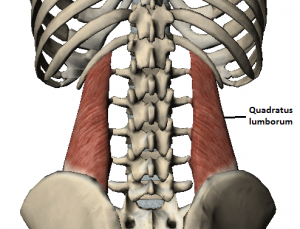
The Quadratus Lumborum is one of the deepest abdominal muscles and is commonly referred to as a back muscle. It is located in the posterior abdominal wall on either side of the lumbar spine and is irregular and quadrilateral in shape. The Quadratus Lumborum starts at the lowest rib and ends at the top of the pelvis in human anatomy.
Quadratus Lumborum Origin
The Quadratus Lumborum muscle originates from the aponeurotic fibers and travels into the iliolumbar ligament and the internal lip of the iliac crest for about 5 centimeters. Seldom, is has been observed to arises from upper borders of the transverse processes of the lower three or four lumbar vertebrae. From here it gets inserted into the lower edge of the last rib for about half its length.
Quadratus Lumborum Structure
The Quadratus Lumborum lies very close to other structures such as the kidney and the colon that are located towards the lower surface of this muscle. It fills a great amount of space within the abdomen. It continues to the lateral abdominal muscle after it exits from the lumbar plexus when the two iliohypogastric and ilioinguinal nerves route on the lower surface of the Quadratus Lumborum. It innervates the ventral primary rami of T12 – L3 and the branches of the lumbar artery supply blood to this muscle.
Quadratus Lumborum Functions
The Quadratus Lumborum is known for its contribution to stabilize and control the movements of other structures like the pelvis and the spine. There are few more functions that it performs which are:
- A two-sided tightening of the Quadratus Lumborum leads to expansion of the lumbar vertebral column. When the muscle gets stimulated on one side, the trunk is bent towards that direction which is called the lateral flexion.
- In addition, it helps in fixing the 12th rib when the thoracic cage movements are in action.
- The Quadratus Lumborum assists the diaphragm in inhalation.
- It helps in elevation of the Ilium bone through the ipsilateral contraction.
Quadratus Lumborum Pictures
Clinical significance
Most commonly, the Quadratus Lumborum is a source of soreness or pain in the lower back of the human body. Since it connects the spine and the pelvis it has the capability of extending the lower back when contracting bilaterally. When the lower fibers of the erector spine are weak or repressed it causes pain too. Constant contractions during continuous seating result in overuse of the Quadratus Lumborum, therefore, causing a muscle fatigue. A constantly contracted Quadratus Lumborum experiences decreased blood flow and over a period of time develops into adhesion of the muscle causing a muscle spasm.
The pain that women face during menstruation is associated with acute hypertonicity and spasms of the Quadratus Lumborum. The pain can be subdued by stretching, and applying pressure in the muscle belly (at the trigger points) may help get some relief. Some other causes of pain are due to damage or imbalance of the pelvis or spine which forces this muscle to stabilize them.
Diagnosis
Pain in Quadratus Lumborum can result in a spread of stress to other areas of the human body. Pain in the Quadratus Lumborum causes pain in hip joints, buttocks, thighs, sacroiliac joint, lower back pain and abdominal pain.
Upon diagnosis, the doctor will ask the patient to perform certain physical activities. Basis the physical examination, the doctor will get to the root of the pain and accordingly advise the course of treatment.
Treatment
The following type of therapies can ease the pain in Quadratus Lumborum muscle:
- Applying heat and ice packs to the trigger points can help in reducing the pain and inflammation.
- Consumption of painkiller or muscle relaxant advised by the doctor can help in reduction of the pain.
- Physiotherapy
- Chiropractic treatment
- Acupuncture
- Yoga therapy
Prevention
Daily exercise and keeping the fitness routine in check can help in the prevention of You Quadratus Lumborum pain. Stretching and strengthening of the muscles in that area during an exercise regime is also advisable. Practicing yoga, Pilates, and tai chi can prove to be effective core strengtheners. Some other guidelines for preventing this pain are:
- Maintaining good posture while standing, sitting, and driving
- Ensuring the correct way of picking heavy stuff
- Sleeping in a correct position that will prove beneficial in reducing back pain.
Often, weak muscles need strengthening because the tightening of muscles is the root cause of pain. Too long sustained contractions result in a reduction of blood flow to the tissues. This is not only the case with other muscles in body but also with Quadratus Lumborum. Once the blood flow is restricted it is hard to perform basic physiological functions. This includes removal of waste products and in addition low supply of oxygen to the muscles resulting in dysfunction. Hence it is advised to follow an exercise regime that helps you in strengthening the muscles and improve blood flow and supply of oxygen to all parts of the body.
Frequently Asked Questions
1. What is the Quadratus Lumborum muscle?
Answer – The Quadratus Lumborum or the QL is the deepest abdominal muscle that is located in the lower back on either side of the lumbar spine. It is the prime source of lower back pain.
2. What causes Quadratus Lumborum pain?
Answer – Pain in Quadratus Lumborum occurs due to overuse, stress, and strain. Stiffness and tightening of this muscle can also result in pain in the lower back area. Sitting for a longer duration, repetitive motions and weaker back muscles also cause pain in the Quadratus Lumborum.
3. What are Trigger points/Pain points in Quadratus Lumborum?
Answer – Trigger point when aroused cause pain. These points occur due to stressed or injured muscles that result in pain and tightness. The trigger points for Quadratus Lumborum pain are because of aches in lower back or stabbing pain in the pelvis and the hips.
4. How is Quadratus Lumborum pain diagnosed?
Answer – A thorough physical examination conducted by the doctor can help in understanding the trigger points of the Quadratus Lumborum pain. The Doctor will make the patient perform various physical activities to understand and describe the nature of damage, stress or any injury.
5. Can Quadratus Lumborum pain cause complications?
Answer – If the pain in the QL goes unnoticed for a longer period of time, it can result in triggering stress to other areas of the body. The pain can become severe and potentially cause pain in hip joints, buttocks, thighs, sacroiliac joint and abdominal pain.

No comments yet.