Vagus Nerve Definition
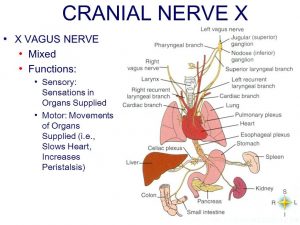
Vagus Nerve (CN 10) which is normally known by the term pneumogastric nerve is counted as the number ten cranial nerve also referred as CN X. It mainly keeps an interaction with the parasympathetic heart control, lungs as well as digestive track of the body.
Vagus Nerve is paired, not once or twice but every time and a pair is normally called a singular. In the autonomic nervous system, the vagus nerve is the longest nerve which is known to science so far. The vagus Nerve also has a concerned function that relates to the peripheral chemoreceptor.
Vagus Nerve Location and Origin
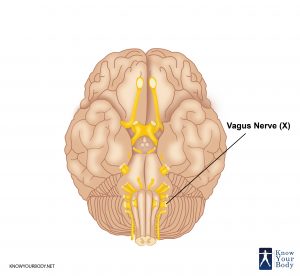
Vagus nerve begins in the medulla. Its roots go to the jugular foramen. Within the hole are nodose and jugular sensory ganglia that pass from the lateral portion of the skull. The vagus nerve is considered as part of the carotid sheath. Its anterior parts include internal jugular vein and carotid artery. This nerve comprises esophageal plexus and pierces diaphragm and enters deep into the abdominal viscera.
Vagus Nerve Types
The different types of the vagus nerve are distributed all over the nervous system and consist of:
- The Right vagus nerve
- The Light vagus nerve
Vagus Nerve Function
It is a part of the nervous system that controls the unconscious body activities, including the maintenance of the heart rate. A vagus nerve enjoys the control of your heart, lungs, and digestive tract. This 10th cranial nerve is found in pairs in the human body.
A vagus nerve function covers everything starting from involuntary actions to the voluntary ones. It helps you in proper breathing by keeping the larynx open while you breathe or respire. When you sweat that’s because your vagus nerve is functioning well. It monitors and maintains your heartbeat. From minor bodily functions to driving major communication within the body, vagus nerve function includes everything in the list. It informs the brain about the indigested as well as digested food. Given to the above-mentioned functions that vagus nerve carries out, it is clear that if the nerve gets damaged, it will affect the overall voluntary as well as involuntary functions of a human body. It is advised to people suffering from high blood sugar to control the rise in the levels to make sure their vagus nerve works properly.
Vagus Nerve Structure
The vagus nerve is the 10th cranial nerve and is primarily linked to the parasympathetic part of the autonomic nervous system. But, it also holds some sympathetic nature through the peripheral chemoreceptors. It is a mixed nerve that contains both efferent and afferent motor fibers. This implies that it is responsible for not only transmitting the motor signals to the organs but it also transmits the sensory information from the organs back to the central nervous system. The structure of vagus nerve contains:
- Special Sensory
- General Afferent Fibers
- Visceral Afferent Fibers
- Visceral Efferent Fibers
- Branchial Efferent Fibers
Vagus Nerve Anatomy
It is the longest cranial nerve containing sensory and motor fibers. It moves through neck, thorax, and then to the abdomen. It composes visceral afferent and somatic fibers along with special visceral and general efferent fibers.
Vagus Nerve from the Brain
This nerve exits from the brain from medulla oblongata in the area between the inferior cerebellar peduncle and olive. It leaves the skull from the middle section of the jugular foramen where it holds lower and upper ganglionic swellings that are essential for the nerve movement. The inferior ganglion is bigger in size and is 2.5 cm while the superior ganglion is less than 0.5 cm in diameter. From the inferior ganglion, the vagus nerve connects to the accessory nerve’s cranial root.
Path of Vagus Nerve
This nerve moves vertically within the carotid sheath posterolateral to the common and internal carotid arteries. The right vagus intersects in front of the first area of the subclavian artery and then move into the fat in the innominate vessels. Then it extends to thorax from the right side of trachea separating it from the right pleura.
It then moved behind the right lung’s hilum and moves medially towards the esophagus from the esophageal plexus. The left vagus nerve intersects in front of the left subclavian artery to enter the thorax from the subclavian arteries and common carotid. While descending towards the left side of phrenic nerve is separated from the left Leura and move behind the phrenic nerve. The path behind the left lung’s root deviated medially and in a downward direction to reach esophagus and create the esophageal plexus by linking the right vagus nerve.
The posterior and anterior gastric nerves are then created from the esophageal plexus.
Vagus Nerve Divisions in Jugular Foramen
The meningeal branch occurs at the superior ganglion and enters into the craniums from the jugular foramen to serve the posterior fossa dura.
The auricular branch supplies movement to the posterior aspect of the external ear and external auditory canal. It occurs from the superior ganglion and enters into the mastoid canaliculus in the ending part of the jugular foramen. It then exits from the tympanomastoid structure of temporal bone to reach the skin.
Vagus Nerve Divisions in Neck
The different branches of the vagus nerve in the neck are Pharyngeal branches, recurrent laryngeal nerve, superior laryngeal nerve, and superior cardiac nerve.
Vagus Nerve Divisions in Thorax
The ramus cardiac inferiors or the inferior cardiac brans is on the right side. It occurs from the trunk of the vagus and lies beside trachea. From the left side originated the recurrent laryngeal nerve. The divisions end in deep part of cardiac plexus.
Vagus Nerve Division in Abdomen
The gastric branches of vagus nerve supply the stomach. The branches rest on the anterosuperior and posteroinferior surfaces. The rami celiaci also known as celiac branches are obtained from the right vagus nerve. They connect to celiac plexus and serve to the spleen, pancreas, adrenals, kidneys, and intestine.
Vagus Nerve Images
Vagus Nerve Clinical Complications
Diabetes is one of the prime reasons for the nerve damage that can stretch to most of the areas of the body. If there is a continuous increment in the level of the blood sugar, then it can easily alter the nerve chemistry and be the reason behind the damage of the blood vessels that help in supporting the nerve.
Other causes of vagus nerve dysfunction include drinking alcohol and surgical complications.
Vagus Nerve Clinal Complication Symptoms
The symptoms of Vagus Nerve can be experienced on the fact that depends on the nerve being overactive or underactive.
The major symptoms of the vagus nerve are:
- Pain is the most common symptoms; it is then accompanied by cramps in the muscle. The pain can also affect an individual’s walking.
- A few types of research have linked vagus nerve with obesity, often resulting in loss of weight drastically.
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome occurs by the deregulation of the autonomic nervous system.
- The dysfunction of vagus nerve causes serious mood swings leading to mood effects and depression.
- There is a proper connection between anxiety and vagus nerve. The dysfunction of the nerve sometimes ignores the response and leaves it unopposed causing insomnia, heart rate increment and anxiety.
Treatment
After there is a confirmation that the vagus nerve is damaged or has suffered a major disorder, the first step to put forward with is a typical therapy of the nerve which will have the nerve exposed to several electrical pulses that will be required to regulate the signals of the nerve. The symptoms that are caused by the nerve disorder can be cured by taking up Medication.
Diagnosis
The damage to the nerve that is left without a treatment for a long time can cause several issues that might turn more severe with time. If the problem grows to a level turning up further issues like the disabled tasting of food, speech problems etc. That is the good time to see a doctor.
Prognosis
The reports and researchers mention that the complications after the treatment might increase with time. There is a temporary relief provided to the patient after the diagnosis has taken place. The complications stay and penetrate to the major portions of the body causing trouble and issues for future.
Differential diagnosis
A differential diagnosis in such cases is only taken into consideration when the roots reach the medulla and jugular foramen is found in the same. The process of differential diagnosis takes place by removing the stem of the nerve from the stomach and passing it through the lateral side of the skull.
Medication
So far, there has been no medication for vagus nerve. The pain happens out of the blue, and there is no way, to get any medications to serve beforehand.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different organs which have connections with vagus nerve?
The different connections of the vagus nerve are with the brain, and then it is further linked with motor function present in the diaphragm, voice box, heart, and stomach.
What is the effect on the heart rate by vagus nerve?
There is a sudden increase in the blood vessel dilation, and a lowering of the blood pressure is also observed. It can also cause a problem with the blood flow and lead to consciousness.

No comments yet.