Mediastinum Definition
The mediastinum is an undefined anatomic space between the lungs that comprises a group of structures within the thorax and principal tissues of the chest excluding the lungs. It contains trachea (a section of the windpipe) heart, esophagus, cardiac nerves, phrenic, thymus, thoracic duct, and other important vessels including the aorta, which is the largest artery carrying the blood from the left ventricle of the heart to the entire body. It includes all the essential organs in the chest excluding the lungs. The mediastinum also houses numerous nerves and lymph nodes.
Mediastinum Location
The mediastinum is located between the left and right pleura and close to the median sagittal area of the chest. It contains thoracic acid and extends to the vertebral column from the sternum in the front.
Anatomical Borders / Boundaries of Mediastinum
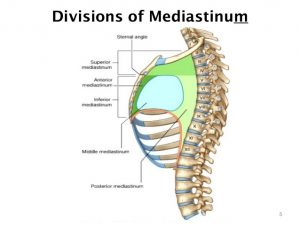
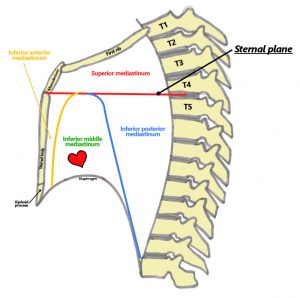
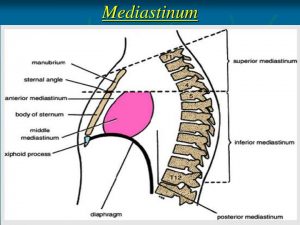
The mediastinum has distinct borders – superior, inferior, posterior, anterior, and lateral.
The lateral borders comprise the medial part of the pleural activities. The inferior boundary of the mediastinum is formed by the diaphragm. The superior boundary is formed by the superior thoracic aperture, which is also known as the thoracic inlet. This inlet is like a bony ring prepared by the primary rib articulating with the first thoracic vertebra posteriorly. Also, the manubrium and costal cartilage are present there. It is even the top-most boundary or region of the mediastinum.
The bodies or components of the thoracic vertebra comprise the posterior border. The anterior wall is made up of the sternum and manubrium. There is also the middle section occupied by the heart, which is known as the middle mediastinum.
Besides these boundaries, the overall structure of the mediastinum is separated into two halves – superior and inferior. These two sections are divided by a transverse plane that passes through the sternal angle to the point of a vertebrate. The superior mediastinum is the upper half while the inferior mediastinum is the lower half. In order to know about the structure of mediastinum, it is essential to get into the details of the superior and inferior mediastinum.
Structure of Mediastinum
The structure of the mediastinum is divided into two categories – superior mediastinum and inferior mediastinum. The lower or inferior mediastinum is further divided into three divisions –middle mediastinum, posterior mediastinum, and anterior mediastinum.
Superior Mediastinum
It is that part of the intrapleural area that rests between the upper thoracic vertebral and manubrium stern from the front. A slightly opaque plan bounds the superior mediastinum. This opaque plan passes backward from the area of the manubrium and the sternum body to the bottom part of the 4th thoracic vertebra. It then passes laterally by the pleura. The various components included in the superior mediastinum are:
• Trachea
• Esophagus
• Veins – It comprises the left highest intercostal vein and the innominate veins. It even comprises the upper half of the vena cava region.
• Thymus
• Great Vessels –It contains the arch of aorta, thoracic parts of the left carotid, and the left subclavian arteries.
• Thoracic Duct
• Vagus and Phrenic nerves and the left recurrent nerves
• Lymph glands
The 3 components of the inferior Mediastinum are as follows:
Anterior Mediastinum
It is the region on the left side of the mediastinum where the left pleura separate from the central-sternal line. This region is bounded by the sternum in the front, pericardium in the front, and pleura in the lateral region. This section is slightly narrow from the above but is slightly widened from the bottom. There are numerous distinct components within the anterior walls of the mediastinum.
• The Thymus Residue
• Fat
• Lymphatic vessels ascending from the convex area of the liver
• Few loose areolar tissue
• Few Mediastinal Lymph Glands
• Small branches of the internal mammary artery
The Posterior Mediastinum
This is a triangular shape and an irregular space running parallel with the column of the vertebral. It is encompassed by the pericardium above and from the diaphragm below. The behind walls of this area is formed by the vertebral column and the lower border is formed by the fourth and the twelfth thoracic vertebra. The other major components of this region are:
• Esophagus
• Descending Aorta
• Lymph glands
• Vagus
• Thoracic duct
• Hemiazygous Veins
• Autonomics
The Middle Mediastinum
This is the biggest region of the intrapleural area that comprises some really imperative components of the heart. The major constituents of this area are as follows:
• Heart
• Ascending Aorta
• Pericardium
• Trachea
• Lymph Nodes
• Pulmonary Veins
• Phrenic Nerves
• Pulmonary Artery
• Trachea
• Bottom region of the Superior Vena Cava
Functions of Mediastinum
The mediastinum is not a human organ meant to perform a function. Rather, it is the space between the lungs and in the center of the chest that comprises numerous components, which have their own respective functions. From the right side, it is bounded by the right pleural, from the left side it is bounded by the left plural, from the bottom it is bounded by the manubrium of the sternum, and from the top, it is bounded by the vertebral column and superior thoracic aperture.
Mediastinum Pictures
Types of Diseases in Mediastinum
It is possible that the mediastinum might experience various severe ailments that can affect the overall functioning of the body and if left untreated they can even result in death.
Thymoma – Tumor of the Thymoma
These are malignant tumors that occur in the thymus gland present in the anterior mediastinum. Thymomas grow slowly and spread to surrounding cells and areas like the pleural space.
Lymphoma – Tumor of the Lymph Node System
Different types of tumors may occur in the lymph node system or the lymphatic region that may occur in the mediastinum. The most common ailments of the lymphoma are the B-cell lymphomas and the Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Mainly, this ailment occurs in the anterior mediastinum, but might also occur in the middle mediastinum.
Germ Cell Tumors
It is tumor occurring in cells that are similar to ovarian or testicular cells that are situated abnormally in the area of the chest.
Masses in the Middle Mediastinum
It is the problem of enlarged lymph nodes. The lymph nodes may get enlarged by an infection, inflammatory process, or malignant.
Masses in the Posterior Mediastinum
It is mainly the tumor or cysts originating from the areas of nerves that are included in the neurogenic tumors or even the tumor from the esophagus.
Myasthenia Gravis
It is an ailment of the junctions where the nerves controlling the muscle functions meet the muscles themselves. In this disease, the antibodies created within the neuromuscular junction make the transmission of the nerve impulses from to the muscles from the nerves. It can lead to numerous problems, such as droopy eyelids, difficulty in breathing and swallowing, double vision, and more.
Treatment Methods
It is possible to treat the Thymoma or the tumor of thymus gland with surgery or a combination of surgery and radiation. Sometimes, it is possible to remove the localized tumors without conducting any preliminary biopsy.
If in case, the thymoma tumor is severe and appear to invade the structure then they need to be treated with chemotherapy and radiation before conducting any surgical removal process. It is essential to first diagnose the tumor through biopsy before conducting a surgical process. The most common form of surgical process to remove thymoma is median sternotomy.
In order to treat lymphoma the process of chemotherapy or radiation therapy is adopted. It is but essential that a precise and prompt surgical biopsy is essential for the successful therapy. Few minimally invasive procedures that are adopted are mediastinoscopy, mediastinotomy, and video-aided thoracoscopic surgery or VATS.
There is a drug therapy available to treat pyridostigmine that can help combat the various symptoms of myasthenia gravis. There are other drugs also recommended like the azathioprine or prednisone to treat this ailment.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Mediastinal Cyst?
There are varieties of mediastinal masses that may develop cystic areas and have varying prognoses. These include bronchogenic cysts, neurenteric cysts, thymic cysts, pericardial cysts, lymphangioma, and cystic teratoma. It is a medical problem that needs to be treated at the earliest; otherwise, it may result in the development of cancer.
What is the meaning of thoracic activity?
Also known as the chest activity, it is the section of the body of vertebrates that is safeguarded by the thoracic wall. The thoracic wall constitutes the skin, ribcage, fascia, and the muscle. The Mediastinum is the central part of the thoracic activity.
Where do Mediastinal masses occur?
Most commonly, the mediastinal masses are the neurogenic tumors that occur in the posterior mediastinum. They are further followed by the thymoma, which occurs in the anterior mediastinum.

No comments yet.