Many organs in our body are responsible for multiple functions. They are responsible for maintaining the balance between different systems of our body and maintain the immune system. Amongst all these useful organs, liver comes in the fourth place of the list. After brain, spinal cord and heart, the liver is that organ in our body that maintains many other systems, indirectly or directly. Liver, though might sound less significant is one such organ that helps in the separation of useful and non-useful substances, aids in maintaining the nutrient balance of the body and many other important processes. As the functions of the liver are varied so is the structure of the organ. Anatomical studies have shown that the liver has one of the most complex histological structures. This is why the study of the organ is somewhat difficult and includes many different biological aspects.
Liver Definition
The liver is an organ concerned with various metabolism and detoxifying roles in the body of the organism. This particular organ is exclusive to the chordates and is absent in invertebrates or lower phylum organisms. The organ almost has the same role in every species, the only difference is in the complexity of both structure and functions. It is a part of the human digestive system and its role concerns the part of assimilation.
It appears reddish brown in appearance because of the immense amount of blood flow to the organ. The change in the color of the human liver indicates the disease of the liver.
Liver Location
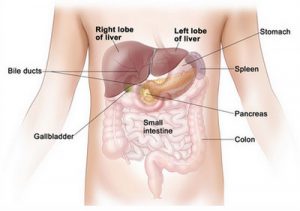
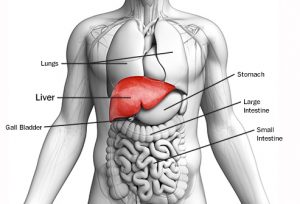
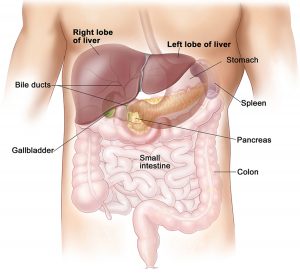
The liver is located in the upper right quadrant of the abdominal cavity, right below the diaphragm. It sits above the right kidney, intestine and the stomach. The rib cage protects this organ. The esophagus or the food pipe passes posteriorly of the organ and enters the stomach situated below it.
Structure of the Liver
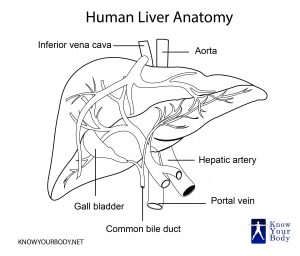
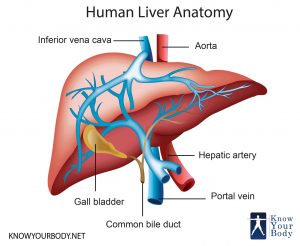
The liver is wedge-shaped and an external view of the organ will reveal that it is made up of four different sized lobes. The liver is designated as the largest gland and the heaviest internal organ of the body. The liver receives two blood vessels- the hepatic artery that supplies oxygenated blood and the hepatic portal vein that supplies broken down nutrients to the liver.
The blood vessels divide into the capillaries that enter the hepatic lobules. The capillaries are known as liver sinusoids.
- The functional unit of the liver is the lobules which are made up of the hepatic cells. These cells are responsible for the metabolic activities and are known as hepatocytes.
- Each lobule is connected to each other by a dense layer of fine connective tissue. This layer is the extension of the capsule that surrounds the liver, Glisson’s capsule.
- A serious layer except at the bare area surrounds the Glisson’s capsule. The serous fluid serves as the lubricating agent for the organ.
- When viewed from the top, the liver is divided into two lobes, the right, and the left lobe, by the falciform ligament.
- The right lobe is the largest amongst the four major segments of the liver.
- However, when viewed from the below, along with the right and the left lobe, there are two other lobes arranged on the divider line of the major two lobes.
- These two small head-on faced lobes are known as the caudate and the quadrate lobes.
- The caudate lobe is the small part that extends from the right lobe in the posterior part. It surrounds the inferior vena cava.
- The quadrate lobe hides the gallbladder from view by wrapping around it. It is located below the caudate lobe.
- Apart from this four lobes, the left lobe is further divided into four segments by the porta hepatis. This makes the liver seven segmented when viewed from the parietal side. However, one can see eight segments from the visceral side.
The liver has many impressions for the attachment of the surrounding organs. The liver secretes bile, which is one of the main digestive juices.
- Bile is secreted by the hepatic cells and drains into the microscopic canals. These canals surround the hepatic lobules and are known as bile canaliculi.
- The canaliculi from various parts of the liver join to form the bile ducts.
- The conglomeration of the numerous bile ducts forms the left and the right hepatic ducts.
- These hepatic ducts join to form the hepatic duct which later on joins with the cystic duct to form the common bile duct.
Liver Functions
The liver is an organ that performs multiple functions related to metabolism, detoxification, and many other roles. The functions of the liver are:
Production of Bile
The liver is the site of the production of bile. Bile is a gastric juice that helps in the emulsification of the fats and also makes the medium in the duodenum alkaline. The sodium bicarbonate salt in the bile neutralize the acidity of the chyme and establishes the required alkaline medium for the pancreatic and intestinal juices to work. This bile is produced by the hepatocytes and carried to the duodenum by the entire biliary tree.
Deamination of the Amino Acids
The amino acids that are supplied to the live rare used for the bodybuilding purposes. The rest of the amino acids are broken down into the amine and acidic part. The amine part is converted into urea and uric acid. This process is known as deamination and liver is the site for the removal of the nitrogenous part from the proteins.
Storing Glucose
The excess glucose in the blood is stored in an active form, glycogen int he liver cells. Insulin aids the conversion of glucose into glycogen via glycogenesis. When there is a need for glucose in the body, the glycogen from the liver is converted into glucose through the process of glycogenolysis. Hence, the liver acts as the storage house for the glucose.
Conversion of other Nutrients into Glucose
Liver aids in the conversion of other nutrients like fatty acids or amino acids into glucose via the process of glucogenesis. Glycerol is an active component in this process and this is produced by the hepatic cells.
Some other Functions
- The liver is responsible for the production of red blood cells in the fetus. This occurs until the heart is developed.
- It is also responsible for the production of thrombopoietin, a protein that helps in the production of thrombocytes by the red bone marrow.
- The liver acts as the site for the breakdown of red blood cells. The iron part of the RBCs is retained in the blood while the protein is broken down into bilirubin and biliverdin.
Innervations of the Liver
The innervation of the liver is largely controlled by the hepatic nervous plexus. This nervous plexus is the receiving center for both the sympathetic nerve fibers and parasympathetic nerve fibers. The parasympathetic nerves are supplied by the vagus nerve while celiac plexus is the source of the sympathetic bundle.
Liver Pictures
Liver Clinical Significance
- Hepatitis: inflammation of the liver
- Cirrhosis: hardening of the liver muscles is a symptom of the cirrhosis. This causes the liver to function improperly.
- Liver cancer: hepatocellular carcinoma is the major type of liver cancer that develops after the cirrhosis.
- Ascites: this is a medical condition where hardened muscles of the liver exude liquid into the stomach. This causes accumulation of the fluid in the abdominal cavity.
- Hemochromatosis: deposition of iron in the liver is the main cause of hemochromatosis.
Liver FAQs
Does any abnormality of the liver functioning can be termed as the liver disease?
Yes, the abnormal function of the liver indicates the development of liver disease.
What is the first and prime symptom of any liver disease?
Increase in the production of bile is the main symptom of the liver disease. This condition is termed as jaundice. The bile pigments appear in the urine of the person. The white part of the eye turns yellowish along with the tongue and nails.
What is hepatitis?
Hepatitis is a medical condition that causes the inflammation of the liver cells. This can be caused by any viral infection or any other factors like excess alcohol abuse.
Is liver cirrhosis fatal?
Liver cirrhosis is the condition where the liver stops functioning properly. Hence this turns fatal as it leads to hepatic cancer and also the accumulation of fluid in the abdomen.
what side of the body is your liver located on?
The liver is located on the right side of the human body.
Can you live without a liver?
No, you can not live without a liver, you might survive for 2-4 days depending on the case if the liver is removed surgically. Generally, a small portion of the liver is donated to the patient, the liver grows back to the normal size over time.

No comments yet.